7 Proven Steps: PQC in CI with ML-KEM Gate & CBOM
Engineering leaders don’t need more theory—you need merge-blocking controls and audit-ready artifacts. This guide shows how to operationalize PQC in CI by shipping two core capabilities:
- A cryptography bill of materials (CBOM) that inventories algorithms, key sizes, and crypto libraries across code, containers, and services.
- A merge gate for ML-KEM readiness (a.k.a. Kyber) that prevents new quantum-vulnerable tech debt, supports hybrid KEM planning, and proves crypto-agility for audits.
You’ll get runnable snippets for GitHub Actions/GitLab CI, OPA/Rego policies, and lightweight scanners you can adapt in a sprint.
If you’re looking for practical ways to bake audits into your delivery pipeline, don’t miss our article on embedded compliance in CI/CD: https://www.cybersrely.com/embedded-compliance-in-ci-cd-tactics/
What you’ll build
- CBOM pipeline: repo + container scanning with JSON output (per service).
- Crypto policy with allowed/disallowed primitives and key floors.
- ML-KEM readiness gate to block merges that add quantum-vulnerable usage without waivers.
- Exception registry with time-boxed waivers + SOC 2/ISO 27001/PCI mapping.
- Evidence pack: signed CI logs, policy commit hash, CBOM snapshot, and exception ledger.
Step 1 — Build a CBOM (code, containers, services)
Create a repo-local scanner to enumerate algorithms, key sizes, and libraries. Treat it like an SBOM, but for cryptography.
tools/cbom_scan.py (Python 3.11)
#!/usr/bin/env python3
import os, re, json, glob, hashlib
from pathlib import Path
ALG_PATTERNS = {
# algorithms (extend as needed)
"md5": r"\bmd5\b",
"sha1": r"\bsha1\b",
"sha256": r"\bsha-?256\b|\bSHA256\b",
"sha3_256": r"\bsha3[-_]?256\b",
"des": r"\bdes(_?ede3)?\b|\b3des\b|\btriple[-_]?des\b",
"rc4": r"\brc4\b",
"aes_ecb": r"aes[-_]?ecb",
"aes_gcm": r"aes[-_]?gcm",
"chacha20_poly1305": r"chacha20[-_]?poly1305",
"rsa": r"\brsa\b",
"ecdsa": r"\becdsa\b",
"x25519": r"\bx25519\b",
"ml_kem": r"\b(ml[-_]?kem|kyber(512|768|1024))\b"
}
LIB_HINTS = [r"pyca/cryptography", r"OpenSSL", r"wolfSSL", r"BoringSSL", r"libsodium", r"NaCl", r"mbedTLS", r"liboqs"]
# file globs to inspect
GLOBS = ["**/*.py","**/*.js","**/*.ts","**/*.go","**/*.java","**/*.rs","**/*.c","**/*.cpp","**/*.cs","**/*.rb","**/*.php","**/*.scala"]
def scan_file(path):
text = Path(path).read_text(errors="ignore")
hits = []
for name, rgx in ALG_PATTERNS.items():
m = re.findall(rgx, text, flags=re.I)
if m:
hits.append({"algo": name, "count": len(m)})
libs = []
for hint in LIB_HINTS:
if re.search(hint, text, re.I):
libs.append(hint)
return hits, list(set(libs))
def key_size_guess(path, text):
# rough key floor detection; extend for your stack
ks = []
for m in re.finditer(r"RSA\W*(\d{3,5})", text, re.I):
ks.append({"algo": "rsa", "bits": int(m.group(1))})
for m in re.finditer(r"(P-256|P-384|P-521|ed25519|x25519)", text, re.I):
ks.append({"algo": "ec", "curve": m.group(1)})
return ks
def scan_repo(root="."):
results = []
for pattern in GLOBS:
for f in glob.glob(os.path.join(root, pattern), recursive=True):
try:
txt = Path(f).read_text(errors="ignore")
except Exception:
continue
algos, libs = scan_file(f)
ks = key_size_guess(f, txt)
if algos or libs or ks:
results.append({"file": f, "algos": algos, "libs": libs, "key_hints": ks})
return results
if __name__ == "__main__":
out = {
"service": os.environ.get("SERVICE_NAME","unknown"),
"commit": os.environ.get("GIT_COMMIT",""),
"findings": scan_repo(),
"container_libs": [], # to be filled by Step 1b
"ts": os.popen("date -Iseconds").read().strip()
}
print(json.dumps(out, indent=2))Containers: add a tiny inspector that prints crypto libs present in images.
tools/cbom_container.sh
#!/usr/bin/env bash
set -euo pipefail
IMG="${1:-app:latest}"
tmp=$(mktemp -d)
cid=$(docker create "$IMG" sh -c 'true')
docker export "$cid" | tar -C "$tmp" -xf -
docker rm "$cid" >/dev/null
# naive scan for library names / providers
grep -R -Ei 'lib(ssl|crypto|oqs)|oqsprovider|wolfssl|mbedtls|libsodium' "$tmp" | cut -d: -f1 \
| sort -u | head -n 200 > cbom_container_libs.txt
jq --argfile libs <(jq -R -s 'split("\n")|map(select(length>0))' cbom_container_libs.txt) \
'.container_libs = $libs' cbom.json > cbom.out.json || cp cbom.json cbom.out.jsonGitHub Actions (extract + publish CBOM)
name: cbom
on: [push, pull_request]
jobs:
make-cbom:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
steps:
- uses: actions/checkout@v4
- name: Python deps
run: pipx install jq && python -V
- name: Run CBOM scanner
env: { SERVICE_NAME: usersvc, GIT_COMMIT: ${{ github.sha }} }
run: |
python tools/cbom_scan.py > cbom.json
- name: (optional) Container CBOM
run: |
docker build -t app:ci .
bash tools/cbom_container.sh app:ci || true
- name: Upload CBOM
uses: actions/upload-artifact@v4
with: { name: cbom-${{ github.sha }}, path: cbom*.json }Free Website Vulnerability Scanner — Landing
Step 2 — Define a crypto policy (one file, reviewable)
policy/crypto-policy.yaml
version: 1
allowed_primitives:
# plan for hybrid today, ML-KEM soon; adapt to org roadmap
key_establishment: ["ECDH-P256+ML-KEM-768", "X25519+ML-KEM-768", "ML-KEM-768"]
bulk_cipher: ["AES-GCM-128","AES-GCM-256","CHACHA20-POLY1305"]
hash: ["SHA-256","SHA-384","SHA3-256","SHA3-384"]
signature: ["Ed25519","ECDSA-P256","ML-DSA-65"] # transitional + target
disallowed:
- "MD5" # collision-broken
- "SHA-1" # collision-broken
- "DES" # weak
- "RC4" # weak
- "AES-ECB" # malleable
floors:
rsa_min_bits: 3072
ecc_allowed_curves: ["P-256","P-384","X25519"]
classify:
quantum_vulnerable:
- "RSA"
- "ECDH"
- "ECDSA"
waiver:
max_days: 180
needs:
- owner
- reason
- compensating_controls
- exit_byKeep this as code in the repo so changes go through PRs like any other policy.
Step 3 — Gate disallowed primitives in CI
Use OPA/Rego to read the CBOM and fail merges if policy violations exist without a valid waiver.
policy/cbom.rego
package cbom.gate
default deny := []
# Input shape: { "cbom": {...}, "policy": {...}, "waivers": [...] }
violation[v] {
f := input.cbom.findings[_]
a := f.algos[_]
banned := input.policy.disallowed[_]
lower(a.algo) == lower(banned)
v := {"file": f.file, "reason": sprintf("Disallowed primitive: %s", [a.algo])}
}
weak_rsa[v] {
f := input.cbom.findings[_]
k := f.key_hints[_]
k.algo == "rsa"
k.bits < input.policy.floors.rsa_min_bits
v := {"file": f.file, "reason": sprintf("RSA key too small: %d", [k.bits])}
}
quantum_vuln[v] {
f := input.cbom.findings[_]
a := f.algos[_]
qv := input.policy.classify.quantum_vulnerable[_]
lower(a.algo) == lower(qv)
not has_valid_waiver(f.file)
v := {"file": f.file, "reason": "Quantum-vulnerable usage without waiver"}
}
has_valid_waiver(file) {
w := input.waivers[_]
w.file == file
now := time.now_ns()
ttl := input.policy.waiver.max_days * 24 * 3600 * 1e9
now - time.parse_rfc3339_ns(w.expires) < ttl
}
deny := concat_array([violation, weak_rsa, quantum_vuln])Waiver ledger (time-boxed, reviewable)
exceptions/waivers.yaml
- file: "svc/payments/legacy_rsa.go"
owner: "payments-team"
reason: "Legacy partner requires RSA-2048; migration scheduled."
compensating_controls: ["TLS 1.3 only", "short-lived certs", "rate-limit"]
expires: "2026-03-31T23:59:59Z"CI step (GitHub Actions)
- name: Evaluate CBOM against policy
run: |
pipx install yq
jq -n --slurpfile c cbom.json \
--argfile p policy/crypto-policy.yaml \
--argfile w exceptions/waivers.yaml \
'{cbom:$c[0], policy:$p, waivers:$w}' > input.json
curl -L -o opa https://openpolicyagent.org/downloads/latest/opa_linux_amd64
chmod +x opa
./opa eval -I -f pretty -i input.json -d policy 'data.cbom.gate.deny' | tee deny.txt
if grep -q '{' deny.txt; then
echo "::error::CBOM policy violations found"
exit 1
fiStep 4 — Add an ML-KEM readiness gate
The aim is to prove crypto-agility and prevent new debt. Start with configuration and dependency signals, then evolve to runtime validation.
Option A — Dependency/config signals (fastest)
Require any service handling key establishment to declare a PQC plan.
crypto.yml (per service)
service: usersvc
key_establishment_target: "ECDH-P256+ML-KEM-768" # target hybrid
status:
runtime_lib: "OpenSSL-3.x"
pqc_provider: "oqsprovider" # or "none" if not yet enabled
rollout: "pilot" # pilot | partial | full
milestones:
enable_provider_in_staging: "2026-01-31"
hybrid_kem_in_prod: "2026-06-30"CI check: block merges that introduce new ECDH/RSA usage without an ML-KEM plan.
# tools/mlkem_gate.sh
set -euo pipefail
git diff --name-only origin/main...HEAD | xargs -I{} grep -nE 'ECDH|RSA' {} | tee kem_hits.txt || true
plan=$(yq '.key_establishment_target' crypto.yml)
if [ -s kem_hits.txt ] && ! grep -qi 'ML-KEM' <<< "$plan"; then
echo "::error::New key-establishment usage without ML-KEM plan in crypto.yml"
exit 1
fiOption B — Runtime provider presence (when feasible)
If you ship OpenSSL with OQS provider (or equivalent), assert the provider is loadable in CI images.
# minimal provider probe
openssl list -providers 2>/dev/null | grep -i oqs || {
echo "::warning::OQS provider not present; ML-KEM readiness = false"
exit 1
}Option C — Policy-as-code (OPA)
Fail if CBOM contains quantum-vulnerable key establishment and crypto.yml.status.rollout isn’t at least pilot.
policy/mlkem.rego
package pqc.gate
deny[msg] {
some f
f := input.cbom.findings[_]
some a
a := f.algos[_]
lower(a.algo) == "rsa" # or "ecdsa"/"ecdh"
input.crypto.status.rollout == "none"
msg := sprintf("Quantum-vulnerable KE without ML-KEM rollout plan: %s", [f.file])
}Step 5 — Generate a remediation backlog (with exit-by dates)
Turn the CBOM into issues with deadlines aligned to your policy.
# tools/backlog_from_cbom.py
import json, datetime, sys
cbom = json.load(open("cbom.json"))
out = []
deadline = (datetime.date.today() + datetime.timedelta(days=180)).isoformat()
for f in cbom["findings"]:
for a in f["algos"]:
if a["algo"].lower() in ["md5","sha1","des","rc4","aes_ecb"]:
out.append({"title": f"Replace {a['algo']} in {f['file']}",
"labels": ["crypto-remediation","high"],
"exit_by": deadline})
for k in f.get("key_hints", []):
if k.get("algo") == "rsa" and k.get("bits", 0) < 3072:
out.append({"title": f"Rotate RSA key (<3072) in {f['file']}", "labels":["crypto-remediation","med"], "exit_by": deadline})
print(json.dumps(out, indent=2))Pipe this into your ticket API (GitHub, Jira) to auto-create work with clear “exit by” dates.
Step 6 — Produce audit-ready evidence (signed)
Capture and sign policy + CBOM + logs so audits don’t become archaeology.
# scripts/evidence.sh
set -euo pipefail
mkdir -p evidence
cp policy/crypto-policy.yaml evidence/
cp cbom.json evidence/
git rev-parse HEAD > evidence/policy_commit.txt
tar -czf evidence.tar.gz evidence
# sign with cosign keyless or GPG (choose one)
cosign sign-blob --yes evidence.tar.gz > evidence.sig || gpg --armor --detach-sign evidence.tar.gzUpload evidence.tar.gz + signature as build artifacts and reference them in your change record.
Control mapping (examples)
- SOC 2 CC6/CC7: preventive merge gates + detective logs.
- ISO 27001 A.8 / A.14: crypto policy and secure development controls.
- PCI DSS 6 & 10: secure coding checks + logging evidence.
Step 7 — Rollout pattern that works
- Pilot on one critical service (warn-only → block).
- Policy package org-wide (policy + OPA bundles + exception workflow).
- Vendor validation (add to your questionnaire):
- Do your services support ML-KEM (or hybrid) for TLS/KE?
- Provide your crypto policy and exception ledger with expiry dates.
- Share a CBOM snapshot and a plan to exit quantum-vulnerable usage.
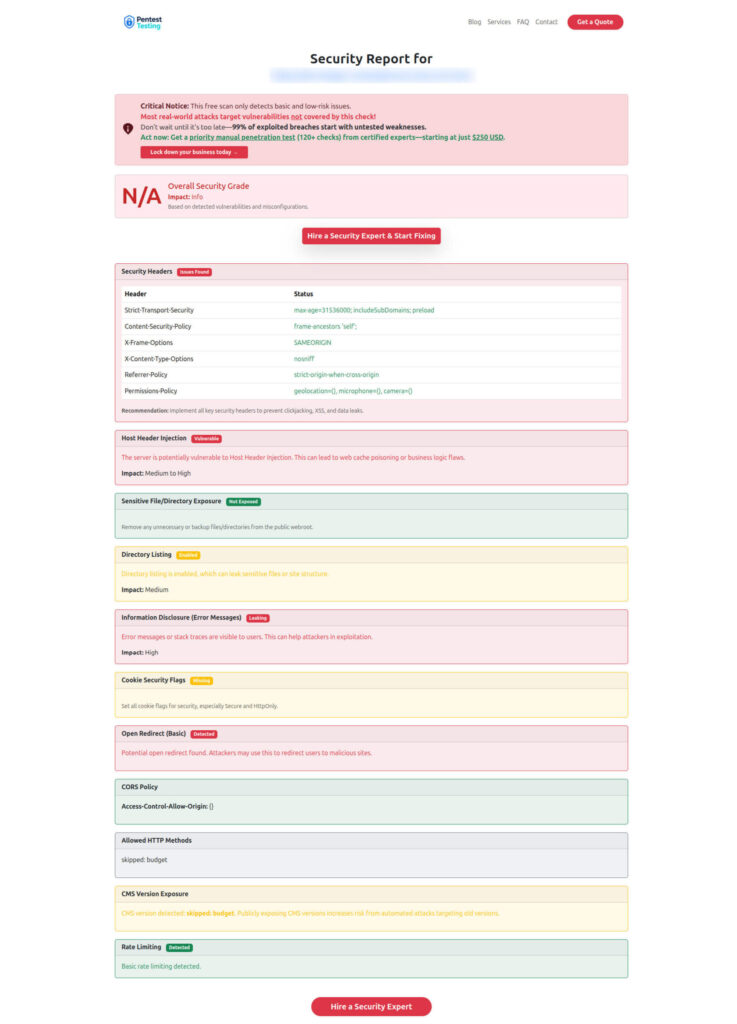
Sample report — Findings excerpt to check Website Vulnerability
When you’re ready for a deeper review or assessor-ready packaging, explore:
- Risk Assessment Services — map CI outputs to SOC 2/ISO/PCI and plan the rollout.
- Remediation Services — close gaps quickly with engineer-friendly fixes.
Risk Assessment Services | Remediation Services | Free Website Security Scanner
GitLab CI equivalents (quick start)
stages: [cbom, policy]
cbom:
stage: cbom
image: python:3.11
script:
- pip install jq yq || true
- python tools/cbom_scan.py > cbom.json
artifacts:
when: always
paths: [cbom.json]
policy:
stage: policy
image: alpine:3.20
script:
- wget -qO opa https://openpolicyagent.org/downloads/latest/opa_linux_amd64 && chmod +x opa
- apk add --no-cache jq yq
- jq -n --slurpfile c cbom.json \
--argfile p policy/crypto-policy.yaml \
--argfile w exceptions/waivers.yaml \
'{cbom:$c[0], policy:$p, waivers:$w}' > input.json
- ./opa eval -I -f pretty -i input.json -d policy 'data.cbom.gate.deny' | tee deny.txt
- test ! -s deny.txtRelated reads on our blog
- 5 Proven CI Gates for API Security: OPA Rules You Can Ship — practical OPA policies + evidence workflow.
- 7 Proven Software Supply Chain Security Tactics — SBOM → VEX → SLSA with copy-paste CI.
- 7 Proven Steps for SSDF 1.1 CI/CD Attestation — wire attestations into builds.
- OWASP GenAI Top 10: 10 Proven Dev Fixes — CI gates for LLM features.
Final note
If you want help wiring PQC in CI with merge-blocking ML-KEM gates, an actionable CBOM, and audit-ready evidence, our team can pair with your engineers, pilot on one service, and expand org-wide without slowing velocity.
Start with a quick perimeter check: Website Vulnerability Scanner Online Free
Need assessor-ready packaging? Risk Assessment Services • Remediation Services
🔐 Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Find answers to commonly asked questions about PQC in CI.