Best 7 Ways to Prevent Cache Poisoning in React.js
🚨 What Is Cache Poisoning in React.js?
Cache Poisoning in React.js is a serious web vulnerability where an attacker tricks a caching server or reverse proxy (like CDN, NGINX, or Varnish) into storing and serving malicious responses. These responses are then delivered to legitimate users, leading to data breaches, unauthorized redirects, or JavaScript injection in the React front-end.

This is particularly dangerous in Single Page Applications (SPAs) like React.js apps because caching is frequently used to improve performance — making these apps prime targets.
🔥 Why You Should Care About Cache Poisoning in React.js
React.js applications use dynamic routing, user-specific content, and third-party APIs — all of which can be exploited if cache behavior is not properly managed.
Cache Poisoning in React.js is commonly triggered through:
- Manipulating HTTP headers like
Host,X-Forwarded-Host, orX-Original-URL - Injecting query parameters that bypass cache-key filters
- Abusing CDN edge locations to spread poisoned responses
👉 This vulnerability can allow attackers to hijack sessions, steal tokens, or even deface your site.
🛠️ Real-World Example of Cache Poisoning in React.js
Let’s say you’re serving this endpoint:
GET https://example.com/product?id=123The CDN caches the content based on id. Now, an attacker makes a request:
GET https://example.com/product?id=123&user=adminIf the cache key does not exclude the user parameter, and the CDN stores this response, then all future users requesting id=123 could get a poisoned response showing admin content.
🧪 Example 1: React.js Code Without Cache Protection
Here’s an unsafe React API call using fetch() that does not sanitize parameters:
const fetchProduct = async (id, user) => {
const response = await fetch(`/api/product?id=${id}&user=${user}`);
const data = await response.json();
return data;
};An attacker could use this API call to include arbitrary parameters, triggering Cache Poisoning in React.js.
✅ Example 2: React.js Code Secured Against Cache Poisoning
You can avoid this by stripping non-essential parameters and validating cache behavior:
const fetchProduct = async (id) => {
const response = await fetch(`/api/product?id=${encodeURIComponent(id)}`);
const data = await response.json();
return data;
};Make sure the server only considers id for caching and ignores everything else.
🧰 Example 3: Use Express Middleware to Normalize Headers
If you’re using Node.js with Express in your backend:
app.use((req, res, next) => {
delete req.headers['x-forwarded-host'];
delete req.headers['x-original-url'];
next();
});Removing these headers prevents attackers from manipulating cache behavior at the edge or reverse proxy.
🖼️ Screenshot 1: Our Free Website Vulnerability Scanner Tool
Use our Website Vulnerability Scanner Tool to instantly detect issues like cache poisoning vulnerabilities, insecure headers, or overly permissive caching rules.
🔍 Detecting Cache Poisoning Vulnerabilities
- Use tools like Burp Suite, Postman, or our Free Scanner.
- Inject unexpected headers like:
X-Forwarded-Host: attacker.comX-Original-URL: /malicious
- Observe if the same poisoned response gets served to other users.
🔎 Screenshot 2: Sample Vulnerability Assessment Report to check Website Vulnerability
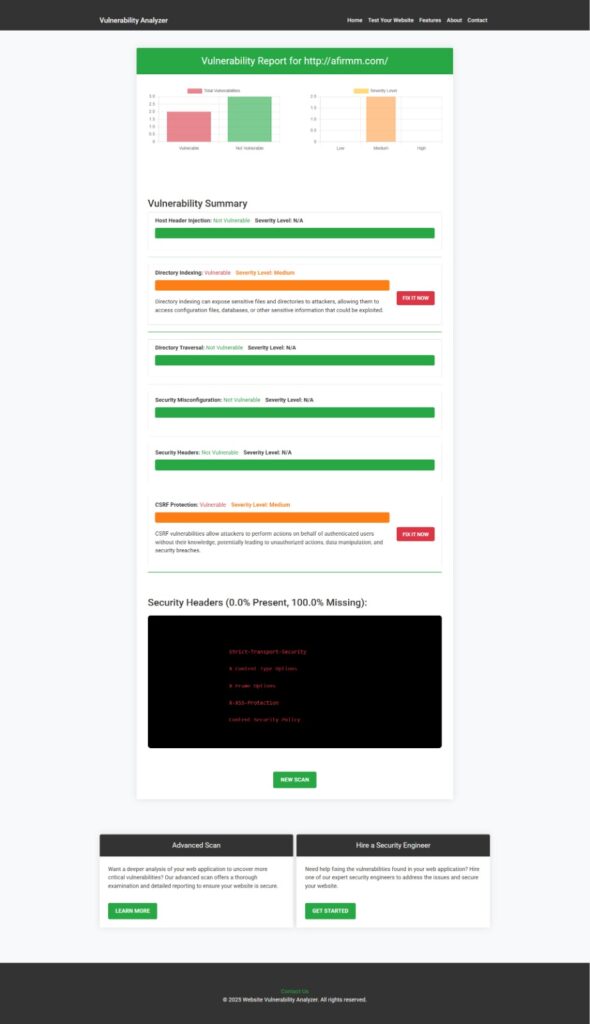
The tool provides a detailed vulnerability report showing caching misconfigurations and HTTP header flaws that could lead to Cache Poisoning in React.js.
🔗 More React.js Security Guides
Explore other React.js vulnerability prevention guides:
- 🛡️ DNS Rebinding Attack in React.js
- 🧩 DNS Rebinding in TypeScript
- 🔐 NoSQL Injection in React.js
- 🚀 Prevent WebSocket Vulnerabilities in React.js
🧠 Secure Your Cache: Best Practices
- ✅ Always sanitize query parameters.
- ⚙️ Configure CDN cache rules strictly.
- 🧾 Use cache keys that exclude user-specific or irrelevant parameters.
- 🚫 Strip harmful headers using NGINX, Express, or Cloudflare rules.
- 🔍 Regularly audit cache behavior with security tools.
- 👨💻 Educate developers on SPA caching risks.
- 🔐 Use token-based API authentication to differentiate users.
🚀 Want Advanced Security for Your AI App?
If you’re working with AI or ML applications using React or Node.js:
👉 Check out our AI Application Cybersecurity Service.
We help detect:
- AI inference poisoning
- Prompt injection via cache
- Misconfigured AI endpoints
🤝 Offer Cybersecurity Services to Your Clients
Are you an agency or MSP?
✅ Become a partner and Offer Cybersecurity to Your Clients with our expert team and white-labeled services.
📬 Need Help? Talk to Us
Facing cache poisoning issues or other frontend threats?
💬 Contact us here and our React security specialists will guide you.
🌐 Related Reading from Pentest Testing
For Laravel developers:
🔐 Prevent Weak API Authentication in Laravel
Want to check your site for free?
🔐 Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Find answers to commonly asked questions about Cache Poisoning in React.js.
Pingback: Prevent WebSocket Vulnerabilities in React.js: Best 7 Ways