Chrome V8 KEV: CVE-2025-10585 Deep Dive
TL;DR (for engineering leaders)
- What: CVE-2025-10585 is a V8 type confusion bug enabling memory corruption via crafted HTML/JS; Google confirmed exploitation in the wild. It’s now in CISA’s KEV with a remediation deadline.
- Fix baseline: Update to Chrome 140.0.7339.185/.186 (Win/Mac) or 140.0.7339.185 (Linux) (released Sept 17, 2025). Newer milestones (M141+) are also rolling out—still ensure your fleet is ≥ the fixed build.
- Scope: Browsers, Android WebView, Electron/Chromium-embedded apps, and any test/CI images shipping headless Chromium. Other Chromium-based browsers (e.g., Opera) shipped fixes shortly after.
- Short-term hardening: Consider Site Isolation, and (for kiosks/specific risk profiles) JIT-less mode to reduce V8 attack surface; expect perf trade-offs.

What CVE-2025-10585 is—and why it’s in KEV
- Vulnerability: Type confusion in V8 (Chromium’s JS/Wasm engine) prior to 140.0.7339.185, allowing remote attackers to exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. Severity High.
- Active exploitation: Google disclosed “exploit exists in the wild” and shipped fixes on Sept 17, 2025. CISA added it to the Known Exploited Vulnerabilities (KEV) on Sept 23, 2025, with a due date of Oct 14, 2025 for federal agencies—use that as your internal SLA.
Impact paths to review
- Enterprise browsers (Chrome/Chromium-based): Push the fixed build; monitor compliance in MDM/Admin consoles.
- Android WebView & embedded WebViews: Devices pick up patched WebView via Play updates; ensure your apps target updated WebView and test flows that embed web content. (Follow Chrome for Android release notes to confirm patched milestones.)
- Electron apps (desktop): Electron embeds Chromium. If your Electron line uses Chromium < 140.0.7339.185, treat as potentially vulnerable; upgrade to a security-bump release once available or rebuild from a patched base. Track the Electron ↔ Chromium mapping during build time.
- Server-side V8 usage: The NVD notes exploitation via crafted HTML in the browser renderer. Server runtimes embedding V8 (e.g., custom engines) should still pull patched V8 when available—especially if executing untrusted JS.
Mitigation steps (patch, backport, harden)
1) Patch to fixed versions
- Chrome Stable: 140.0.7339.185/.186 (Win/Mac) and .185 (Linux). Verify fleet compliance; M141 early-stable also rolling.
- Other Chromium browsers: Track vendor advisories (e.g., Opera confirmed patches); update promptly.
- Electron: Monitor Electron Releases for a tag that includes Chromium 140.0.7339.185+; gate builds until available.
2) Consider temporary hardening (risk-based)
- Site Isolation: Enforce
SitePerProcessto strengthen renderer boundaries during rollout. - Limit JIT (select scenarios): Launch with JIT-less (
--js-flags=--jitless) for kiosks or highly sensitive roles to reduce JIT attack surface. Expect performance impact; don’t deploy broadly without testing. - Admin policies: Chrome Enterprise policies allow org-wide controls and version enforcement; manage via GPO/Intune/Jamf or the Admin Console.
Electron example (main process):
// app entry (main.js)
const { app } = require('electron');
app.commandLine.appendSwitch('js-flags', '--jitless'); // risk-based; expect perf hit(Use only where user experience permits; track crashes/telemetry.)
Screenshot of our Free Website Vulnerability Scanner showing the tool UI:
CI/CD guardrails (stop drift before it ships)
A) Fail builds if a browser dependency is stale
GitHub Action + Node script to enforce minimum Chrome (or CfT) version:
# .github/workflows/chrome-version-guard.yml
name: chrome-version-guard
on: [pull_request]
jobs:
guard:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
steps:
- uses: actions/checkout@v4
- run: npm i -g @puppeteer/browsers
- name: Install Chrome for Testing (stable)
run: npx @puppeteer/browsers install chrome@stable
- name: Enforce minimum Chrome build
run: node ci/check-chrome-version.js// ci/check-chrome-version.js
const { execSync } = require('child_process');
const MIN = '140.0.7339.185';
const out = execSync(`npx @puppeteer/browsers list`, {stdio:['ignore','pipe','ignore']}).toString();
const ver = (out.match(/chrome@stable\\s+([\\d.]+)/) || [])[1] || '0.0.0.0';
function cmp(a,b){const A=a.split('.').map(Number),B=b.split('.').map(Number);for(let i=0;i<4;i++){if((A[i]||0)!==(B[i]||0))return (A[i]||0)-(B[i]||0)}return 0;}
if (cmp(ver, MIN) < 0) { console.error(`Chrome ${ver} < ${MIN} — block merge.`); process.exit(1); }Use Chrome for Testing to deterministically pin browser builds in CI.
B) Electron guard at runtime
// At app start, abort if embedded Chromium is below fixed floor
const min = '140.0.7339.185';
const cur = process.versions.chrome || '0.0.0.0';
// ... reuse cmp() from above ...Check Electron Releases and process.versions.chrome during packaging.
C) Fuzzing gates for your V8 embeddings
Integrate ClusterFuzzLite to fuzz PRs and nightly—use it if you embed V8 or handle complex parsing. Start with Google’s ClusterFuzzLite GitHub Action, or graduate to OSS-Fuzz for continuous coverage.
Fleet enforcement & evidence (IT + SecOps)
- Mandate fixed version via Chrome enterprise update controls; verify via version reports.
- Enable Site Isolation org-wide for sensitive OUs (
SitePerProcess). - Login checks: Simple version checks as GPO/MDM login hooks help catch stragglers quickly.
Windows (PowerShell)
$min=[version]"140.0.7339.185"
$paths=@(
"HKLM:\SOFTWARE\Google\Update\Clients\{8A69D345-D564-463c-AFF1-A69D9E530F96}",
"HKLM:\SOFTWARE\WOW6432Node\Google\Update\Clients\{8A69D345-D564-463c-AFF1-A69D9E530F96}"
)
$ver=$null; foreach($p in $paths){ if(Test-Path $p){ $v=(Get-ItemProperty $p).pv; if($v){ $ver=[version]$v; break }}}
if(!$ver -or $ver -lt $min){ exit 1 } # trigger remediationmacOS (bash/Jamf)
MIN="140.0.7339.185"
OUT=$('/Applications/Google Chrome.app/Contents/MacOS/Google Chrome' --version 2>/dev/null | awk '{print $3}')
[ -z "$OUT" ] && exit 1
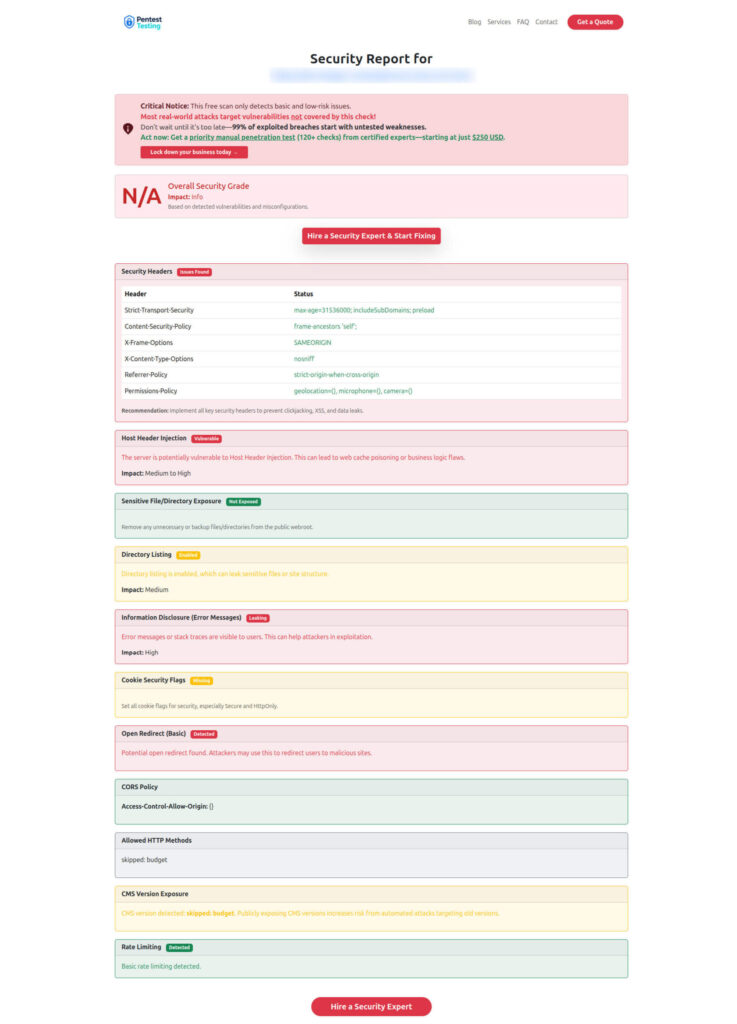
[ "$(printf '%s\n' "$MIN" "$OUT" | sort -V | head -n1)" = "$MIN" ] || exit 1Sample finding from our scanner report to check Website Vulnerability
Add to your CISA & Daily Security Review (the “+2/+2”)
CISA (+2):
- Subscribe/ingest KEV JSON/CSV and raise a blocking ticket for any “Date Added” < 24h.
- Track KEV due dates (here: Oct 14, 2025) against your internal SLA dashboards.
Daily Security Review (+2):
- Delta-check Chrome/Electron version compliance since yesterday; page top offenders.
- Review crash telemetry spikes in renderers and suspicious JS/Wasm in web logs while rolling the fix. (Use Site Isolation as a guardrail.)
- Quick free check: Run our Website Vulnerability Scanner online free to ensure headers/CSP and exposed endpoints aren’t compounding browser-side risk during rollout.
- Deep triage: Book Risk Assessment Services to map Chromium/Chrome for Testing/Electron usage across CI and production, with a prioritized fix plan.
- Hands-on fixes: Our Remediation Services implement policy hardening (Site Isolation), CI pinning, and evidence packs for auditors.
- Dev-centric help: See Web Application Penetration Testing Services (Cyber Rely) and our Laravel pentest case study to align your stack (e.g., Laravel/SaaS).
- Stay current: Follow Pentest Testing Corp Blog and our CVE-2025-10585 write-up, Gate CI with CISA KEV JSON on Cyber Rely for ongoing guidance.
Developer appendix: quick code snippets
Enforce Site Isolation in managed Chrome (policy): see Chrome Enterprise policy list and Admin setup docs to deploy SitePerProcess.
Risk-based JIT reduction: V8 supports jitless mode; use only for kiosks/specific apps due to performance impact.
Final Takeaways
Need a fast, developer-friendly response plan for CVE-2025-10585?
- Start with a free surface scan → free.pentesttesting.com (light, non-intrusive).
- Get a risk assessment mapped to your CI, Electron, and WebView usage → Risk Assessment Services
- Hand off the fixes (policies, CI pinning, evidence) → Remediation Services.
🔐 Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Find answers to commonly asked questions about Chrome V8 KEV: CVE-2025-10585.
Pingback: Gate CI with CISA KEV JSON: Ship Safer Builds