🔒 Best 7 Ways to Fix Weak SSL-TLS Configuration in React.js
Introduction: Why Weak SSL-TLS Configuration in React.js Matters
If your React.js web app is using a weak SSL-TLS configuration, it opens the door for man-in-the-middle attacks, session hijacking, and even sensitive data leaks. In modern web security, HTTPS is non-negotiable, but just enabling it isn’t enough — misconfigured SSL/TLS can be almost as bad as none.

In this guide, we’ll cover the best 7 ways to fix weak SSL-TLS configuration in React.js, with actionable examples developers can apply right away. We’ll also demonstrate how to check your configuration using free tools like our Website Security Checker.
We’ll also link to our in-depth related blogs, such as:
- Fix Insecure Deserialization in React.js
- Path Manipulation Vulnerability in React.js
- Fix CORS Misconfigurations in React.js
- Prevent Path Manipulation in TypeScript
Common Weak SSL-TLS Configuration Issues in React.js
Before jumping into fixes, let’s understand some common mistakes:
- Using outdated TLS versions (like TLS 1.0/1.1).
- Supporting weak ciphers like RC4 or DES.
- Not enabling HSTS.
- Serving mixed content (both HTTP and HTTPS).
- No certificate pinning.
These can make your secure site look HTTPS-enabled but still vulnerable.
🛠️ Best 7 Ways to Fix Weak SSL-TLS Configuration in React.js
Here are 7 actionable fixes for developers working with React.js apps hosted on Node.js, Nginx, or Apache.
1️⃣ Enforce HTTPS and Redirect HTTP
In your React.js app (served by Express), always redirect HTTP requests to HTTPS.
app.use((req, res, next) => {
if (!req.secure) {
return res.redirect('https://' + req.headers.host + req.url);
}
next();
});You can also enforce HTTPS in your frontend by updating package.json for development.
"start": "HTTPS=true react-scripts start"2️⃣ Use TLS 1.3 or TLS 1.2 Only
When configuring your server (e.g., Nginx), specify only modern protocols:
ssl_protocols TLSv1.2 TLSv1.3;
ssl_prefer_server_ciphers on;Remove deprecated versions:
ssl_protocols TLSv1 TLSv1.1; # 🚫 Don't use3️⃣ Enable HTTP Strict Transport Security (HSTS)
Add HSTS headers in your React.js app’s server to ensure browsers use HTTPS:
const helmet = require('helmet');
app.use(helmet.hsts({
maxAge: 31536000,
includeSubDomains: true,
preload: true
}));Or via Nginx:
add_header Strict-Transport-Security "max-age=31536000; includeSubDomains" always;4️⃣ Remove Weak Ciphers
Use only strong ciphers in your Nginx/Apache configuration:
ssl_ciphers 'ECDHE-ECDSA-AES256-GCM-SHA384:ECDHE-RSA-AES256-GCM-SHA384';
ssl_prefer_server_ciphers on;You can test supported ciphers using OpenSSL:
openssl s_client -connect yourdomain.com:443 -cipher RC4If it still connects, you’ve got work to do!
5️⃣ Avoid Mixed Content
Your React components should reference only HTTPS resources. For example:
✅ Good:
<img src="https://yourcdn.com/image.jpg" />🚫 Bad:
<img src="http://yourcdn.com/image.jpg" />You can also add Content-Security-Policy headers to block mixed content:
app.use(helmet.contentSecurityPolicy({
directives: {
defaultSrc: ["'self'"],
upgradeInsecureRequests: []
}
}));6️⃣ Use Certificate Pinning (Optional)
Certificate pinning adds an extra layer of trust by hardcoding expected certificate fingerprints. While React.js itself doesn’t handle this directly, you can implement it at the service worker level or backend.
// Example: validate certificate thumbprint
if (serverCert.fingerprint !== expectedFingerprint) {
throw new Error('Invalid certificate!');
}7️⃣ Regularly Test and Monitor
You can start by running your site through our website vulnerability scanner. Below is a sample screenshot of our tool’s webpage to guide you:
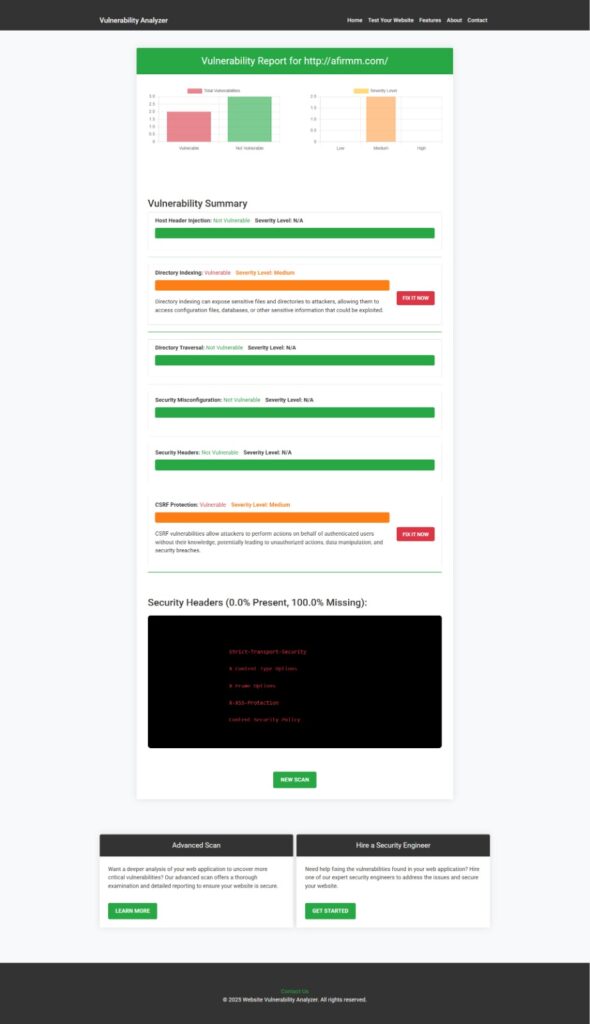
Run periodic scans with our free tools to check website vulnerability. Below is a screenshot of a vulnerability assessment report generated by our tool:
🔗 Learn More: Prevent NoSQL Injection in Laravel
If you also work with Laravel on the backend, don’t miss our article on how to prevent NoSQL injection in Laravel.
Why Weak SSL-TLS Configuration in React.js Must Be Fixed
Fixing weak SSL-TLS configuration in React.js protects:
- User privacy and data integrity.
- Compliance with PCI-DSS, GDPR, HIPAA.
- SEO ranking (Google prefers secure sites).
Our Web Application Penetration Testing Services
If you’d rather leave it to the experts, check out our Web App Penetration Testing Services to get a full security audit of your application and fix all SSL/TLS weaknesses.
Offer Cybersecurity Services to Your Clients
Are you an agency or a freelancer? Partner with us through our Cybersecurity Service Partnership Program and offer SSL/TLS hardening and other services to your clients under your brand.
Get in Touch With Us
Have questions? Contact our experts anytime via our Contact Us page. We’re here to help you secure your React.js apps from the ground up.
Conclusion
Don’t let a weak SSL-TLS configuration in React.js undermine your hard work. By following the 7 best practices shared above — from enforcing HTTPS to disabling weak ciphers — you can harden your app’s security and protect your users.
Run a free scan today with our tool for a Website Vulnerability test and start fixing vulnerabilities now.
Pingback: Fix CORS Misconfigurations in React.js: 7 Proven Ways