Best 7 Tips for SQLi Prevention in React.js (with Examples)
Introduction to SQL Injection (SQLi) in React.js
When building modern web applications with React.js, developers often assume that frontend technologies are immune to backend threats like SQL Injection (SQLi). However, SQLi can still pose serious risks when React interfaces with vulnerable backend services through REST APIs or GraphQL.

In this guide, we’ll explore what SQL Injection in React.js looks like, provide real-world code examples, and share the best 7 actionable tips to prevent it.
This post is part of our continuous effort to raise awareness about modern web vulnerabilities. You may also be interested in our earlier security articles such as:
- How to Prevent CRLF Injection in TypeScript
- Prevent Cross-Site Scripting in React.js
- Prevent JWT Attacks in TypeScript ERP
- How to Prevent XSS in RESTful APIs
📸 Screenshot of Our Website Vulnerability Scanner Tool
Our free tool detects SQL Injection, XSS, CSRF, and other vulnerabilities in seconds
What is SQL Injection (SQLi)?
SQL Injection is a vulnerability that allows an attacker to interfere with the queries an application makes to its database. Although React.js doesn’t directly interact with databases, insecure backend integrations can open the door to SQLi.
Why React Developers Must Care About SQLi
React apps often communicate with APIs that execute SQL queries. If user inputs are not validated and sanitized properly before reaching the backend, attackers can inject malicious SQL.
Example Scenario:
// React frontend
const loginUser = async (username, password) => {
await fetch("/api/login", {
method: "POST",
body: JSON.stringify({ username, password }),
headers: { "Content-Type": "application/json" },
});
};If the backend doesn’t handle inputs safely, SQLi can occur.
7 Tips for SQLi Prevention in React.js
1. Use Parameterized Queries in Backend (Node.js + MySQL)
Always use parameterized queries in your Node.js backend.
❌ Vulnerable Code:
const query = `SELECT * FROM users WHERE username = '${username}' AND password = '${password}'`;✅ Safe Code:
const query = "SELECT * FROM users WHERE username = ? AND password = ?";
connection.query(query, [username, password]);2. Input Validation in React Before Sending Data
Client-side validation helps reduce junk input but shouldn’t replace backend validation.
✅ Example in React:
const validateInput = (input) => /^[a-zA-Z0-9_]+$/.test(input);if (!validateInput(username)) {
alert("Invalid characters in username!");
return;
}3. Use ORM Libraries (e.g., Sequelize)
ORM tools like Sequelize prevent SQLi by abstracting raw queries.
✅ Sequelize Example:
User.findOne({
where: {
username: req.body.username,
password: req.body.password
}
});4. Escape Data Properly in Backend
Use escaping libraries to neutralize special characters.
✅ Example using mysql2:
const escapedUsername = connection.escape(username);5. Limit Query Permissions and Avoid Root Database Access
Grant only the necessary permissions to the DB user.
✅ Example:
GRANT SELECT, INSERT, UPDATE ON app_db.* TO 'app_user'@'localhost';6. Set Web Application Firewall (WAF)
WAFs can block malicious payloads from ever reaching your app.
7. Scan Your Website Using Our Free Tool
We offer a free tool that helps detect SQLi, XSS, and more.
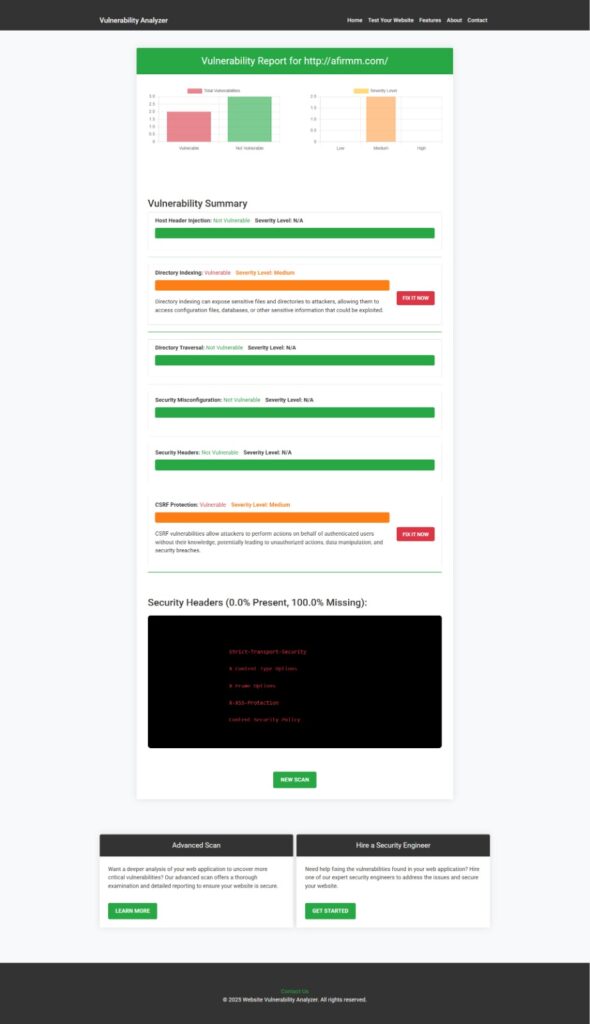
Try it now: Free Website Security Scanner
Full SQLi Vulnerable to Secure Example in React.js + Express
// React: vulnerable fetch call
fetch("/api/search?user=" + input);
// Express backend - vulnerable
app.get("/api/search", (req, res) => {
const query = `SELECT * FROM users WHERE username = '${req.query.user}'`;
db.query(query, (err, results) => res.json(results));
});✅ Secure Version:
// React: keep same, apply validation before sending
const input = sanitizeInput(userInput); // assume sanitizeInput defined
fetch("/api/search?user=" + input);// Express: use parameterized queries
app.get("/api/search", (req, res) => {
const query = "SELECT * FROM users WHERE username = ?";
db.query(query, [req.query.user], (err, results) => res.json(results));
});🔗 Related Resource from Our Partner Site
Also check out: Prevent XXE Injection in Laravel
It’s another great guide for securing backend systems against common attacks.
Conclusion
Even though React.js runs in the browser, SQL Injection risks emerge when insecure backend APIs are involved. Developers must understand the full stack to properly defend against SQLi. Use parameterized queries, input validation, ORM, and regular vulnerability assessments using tools like ours for Website Security check.
For further help, feel free to contact us here.
Pingback: Prevent Cross-Site Scripting in React.js with Best 7 Ways
Pingback: Prevent Broken Access Control in React.js - Best 7 Ways