PCI DSS 4.0.1 Remediation: 7 Proven Patterns Devs Can Ship Today
Angle: With future-dated PCI DSS v4.0.x requirements having been mandatory since March 31, 2025, this guide turns payment-app/API gaps into backlog-ready changes.
PCI Perspectives
PCI DSS 4.0.1 clarifies 4.0 without removing your obligations. If you handle cardholder data (CDE), you must demonstrate working controls—not just documents. This post shows engineering-first, auditable fixes your QSA will love.

Quick links:
• Website Vulnerability Scanner Online free
• PCI DSS Readiness (Pentest Testing Corp)
• PCI DSS Remediation Services (Pentest Testing Corp)
New: OWASP GenAI Top 10 — Real Dev Fixes (2025). Ship prompt-injection guards, output allow-lists, retrieval isolation, and CI gates today. Read the guide: https://www.cybersrely.com/owasp-genai-top-10/
The 7 PCI DSS 4.0.1 Remediation Patterns (Summary)
- Strong MFA everywhere for CDE access (admins, jump hosts, CI, break-glass)
- Eliminate default/test creds; centralize & rotate secrets
- Encrypt in transit with modern TLS; disable legacy ciphers
- Automate cert renewals; store machine-readable evidence
- Segment the CDE; codify allow-lists as code
- Gate builds with SAST/DAST/SCA; fail on criticals; keep change-control artifacts
- Start with an external exposure sweep using our free scanner; publish the backlog
1) Strong MFA for all CDE access (admins, CI, break-glass)
Goal: Every path into the CDE uses phishing-resistant MFA (FIDO2/WebAuthn), short sessions, and device posture.
GitHub (enforce SSO+MFA for admins & runners)
# .github/settings.yml (using Probot Settings or Terraform for GH)
repository:
name: payments-gateway
default_branch: main
branches:
- name: main
protection:
required_linear_history: true
required_pull_request_reviews:
required_approving_review_count: 2
require_last_push_approval: true
restrictions: null
enforce_admins: true
required_status_checks:
strict: true
contexts: ["ci/sast", "ci/dast", "ci/sca"]
# Organization policies (illustrative): require SSO + MFA for adminsOkta Group Rule (illustrative, admin MFA = FIDO2 only)
{
"type": "GROUP_RULE",
"name": "Admins-Require-FIDO2",
"conditions": { "people": { "users": { "exclude": [] } } },
"actions": {
"assignUserToGroups": { "groupIds": ["00g_admins"] },
"enrollAuthenticators": { "required": ["webauthn", "okta_verify_push"] }
}
}Break-glass account policy
- Stored in a sealed vault; WebAuthn token kept offline; time-bound access; auto-rotate post-use with signed audit trail.
2) Kill default/test creds; centralize & rotate secrets
Goal: No hard-coded secrets; no test123/Password! in CI, images, or code. Use a central KMS/Vault with rotation and short TTLs.
Gitleaks (block secrets at commit time)
# .gitleaks.toml
title = "Block credentials & test users"
[[rules]]
id = "generic-secret"
description = "Generic secret patterns"
regex = '''(?i)(api_?key|secret|token|password|passwd)\s*[:=]\s*['"][^'"]+['"]'''
tags = ["pci", "secrets"]
[[allowlist.paths]]
# Allow testdata mocks only:
regex = '''^testdata/'''Vault: issue short-lived DB creds to apps
# vault/policies/payments.hcl
path "database/creds/payments-role" { capabilities = ["read"] }# Rotate root creds monthly, app gets 1h leases
vault write database/roles/payments-role \
db_name=pg-main \
creation_statements="CREATE USER \"{{name}}\" WITH PASSWORD '{{password}}' VALID UNTIL '{{expiration}}'; GRANT CONNECT ON DATABASE payments TO \"{{name}}\";"# app/startup_secrets.py
import hvac, os
c = hvac.Client(url=os.environ["VAULT_ADDR"], token=os.environ["VAULT_TOKEN"])
creds = c.secrets.database.generate_credentials(name="payments-role")["data"]
os.environ["DB_USER"], os.environ["DB_PASS"] = creds["username"], creds["password"]3) Modern TLS only; disable legacy ciphers (HSTS on)
Nginx (TLS 1.2/1.3, good suites, HSTS, OCSP stapling)
server {
listen 443 ssl http2;
server_name pay.example.com;
ssl_protocols TLSv1.2 TLSv1.3;
ssl_ciphers 'TLS_AES_256_GCM_SHA384:TLS_CHACHA20_POLY1305_SHA256:TLS_AES_128_GCM_SHA256:HIGH:!aNULL:!MD5:!RC4:!3DES';
ssl_prefer_server_ciphers on;
ssl_session_timeout 1d;
ssl_session_cache shared:SSL:50m;
ssl_stapling on;
ssl_stapling_verify on;
add_header Strict-Transport-Security "max-age=31536000; includeSubDomains; preload" always;
add_header X-Content-Type-Options nosniff always;
add_header X-Frame-Options DENY always;
add_header Content-Security-Policy "default-src 'none'; frame-ancestors 'none'; base-uri 'none';" always;
# app upstream...
}Verify weak protocols are gone
# These should FAIL if you've disabled legacy protocols
openssl s_client -connect pay.example.com:443 -tls1_0 </dev/null
openssl s_client -connect pay.example.com:443 -tls1_1 </dev/null
# Quick header checks (HSTS/CSP/XFO)
curl -sI https://pay.example.com | grep -Ei 'strict-transport|content-security|x-frame'HAProxy (alternative)
frontend fe_tls
bind :443 ssl crt /etc/ssl/pay.pem alpn h2,http/1.1
ssl-default-bind-options no-sslv3 no-tlsv10 no-tlsv11 prefer-server-ciphers
ssl-default-bind-ciphers TLS_AES_256_GCM_SHA384:TLS_CHACHA20_POLY1305_SHA256
default_backend be_app4) Automate cert renewals; store CI evidence
ACME renewal (acme.sh)
acme.sh --issue -d pay.example.com --nginx
acme.sh --install-cert -d pay.example.com \
--key-file /etc/ssl/pay.key --fullchain-file /etc/ssl/pay.crt \
--reloadcmd "systemctl reload nginx"Evidence: GitHub Actions artifact + JSON log
# .github/workflows/tls-evidence.yml
name: TLS Evidence
on:
schedule: [{ cron: "0 3 * * 1" }] # weekly
jobs:
check:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
steps:
- name: TLS probe
run: |
set -e
OUT=tls-evidence.json
T=$(date -u +%FT%TZ)
HSTS=$(curl -sI https://pay.example.com | grep -i strict-transport || true)
O11=$(echo | openssl s_client -connect pay.example.com:443 -tls1_1 2>/dev/null || true)
jq -n --arg time "$T" --arg hsts "$HSTS" --arg tls11 "$O11" \
'{time:$time, hsts_present:($hsts|length>0), tls11_works:($tls11|length>0)}' > $OUT
[ -s "$OUT" ] && echo "Wrote $OUT"
- uses: actions/upload-artifact@v4
with: { name: tls-evidence, path: tls-evidence.json }Keep the artifact for your ROC evidence store.
5) Segment the CDE; codify allow-lists as code
Terraform (AWS Security Groups: explicit allow-lists)
resource "aws_security_group" "cde_db" {
name = "cde-db"
description = "Card DB allow-list"
vpc_id = var.vpc_id
ingress {
description = "App -> DB 5432"
from_port = 5432
to_port = 5432
protocol = "tcp"
security_groups = [aws_security_group.cde_app.id]
}
egress {
from_port = 0
to_port = 0
protocol = "-1"
cidr_blocks = ["10.0.0.0/16"] # restrict, no internet
}
tags = { pci_scope = "cde", owner = "payments" }
}Kubernetes NetworkPolicy (namespaced CDE pods only)
apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1
kind: NetworkPolicy
metadata:
name: cde-allow-app
namespace: payments
spec:
podSelector: { matchLabels: { tier: "db", scope: "cde" } }
policyTypes: ["Ingress","Egress"]
ingress:
- from:
- podSelector: { matchLabels: { tier: "app", scope: "cde" } }
ports: [{ protocol: TCP, port: 5432 }]
egress:
- to:
- ipBlock: { cidr: "10.0.0.0/16" }Change control artifact
- Require CODEOWNERS for
infra/cde/**andk8s/payments/**with 2 approvers and a change ticket reference in PR body.
6) SAST/DAST/SCA gates with fail-on-critical + change-control
GitHub Actions (Semgrep + ZAP Baseline + Dependency Scan)
# .github/workflows/security-gates.yml
name: Security Gates (PCI)
on: [pull_request]
jobs:
sast:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
steps:
- uses: actions/checkout@v4
- uses: returntocorp/semgrep-action@v1
with:
config: >-
p/owasp-top-ten
generateSarif: true
publishToken: ${{ secrets.SEMGREP_APP_TOKEN }}
- name: Fail on critical findings
run: |
jq '.runs[].results[] | select(.level=="error")' semgrep.sarif && exit 1 || true
sca:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
steps:
- uses: actions/checkout@v4
- name: Dependency Check
uses: jeremylong/DependencyCheck_Action@v4
- name: Fail on CVSS >= 9
run: |
jq '.dependencies[] | select(.vulnerabilities[].cvssScore>=9)' dependency-check-report.json && exit 1 || true
dast:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
steps:
- uses: actions/checkout@v4
- name: ZAP Baseline
uses: zaproxy/[email protected]
with:
target: "https://staging.pay.example.com"
rules_file_name: ".zap/rules.tsv"
- name: Fail on Highs
run: |
grep -q "High (High)" zap-baseline-report.md && exit 1 || trueChange-control evidence template (commit it)
<!-- .compliance/pci/change-control.md -->
- Change ID: CC-{{PR_NUMBER}}
- Scope: /infra/cde/, /services/payments/
- Risk: Low/Med/High
- Compensating Controls: N/A
- Approvals: @cde-owner, @security
- Evidence: SARIF, ZAP report, dependency-check-report.jsonFor a deeper dive into CI hardening, see our recent posts:
• Add an ASVS 5.0 Gate to CI/CD → /asvs-5.0 Gate-to-ci-cd/
• 5 Blazing Steps to a SEC Item 1.05 Pipeline (Cyber 8-K) → /sec-item-1-05-pipeline-cyber-8-k/
• AI-Generated Code Supply-Chain Risk: 7 Proven Ways → /ai-generated-code-supply-chain-risk/
7) External exposure sweep → backlog with our free tool
Step 1 — Run the free scan
Open Free Website Vulnerability Scanner → free.pentesttesting.com and scan your internet-facing payment domains/subdomains.
Free Website Vulnerability Scanner landing screenshot
Step 2 — Convert findings to a backlog (issue template)
<!-- .github/ISSUE_TEMPLATE/pci-external-scan.md -->
name: "PCI External Scan Finding"
labels: ["pci", "external-scan"]
body:
- type: input
attributes: { label: "Asset", description: "Domain/URL" }
- type: textarea
attributes: { label: "Finding", description: "E.g., Missing HSTS / TLS1.0 open" }
- type: input
attributes: { label: "Evidence", description: "Header/output snippet or screenshot" }
- type: dropdown
attributes: { label: "Severity", options: ["Critical","High","Medium","Low"] }Step 3 — Automate a weekly reminder (simple cron)
# .github/workflows/pci-external-reminder.yml
name: PCI External Scan Reminder
on:
schedule: [{ cron: "0 7 * * 1" }]
jobs:
remind:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
steps:
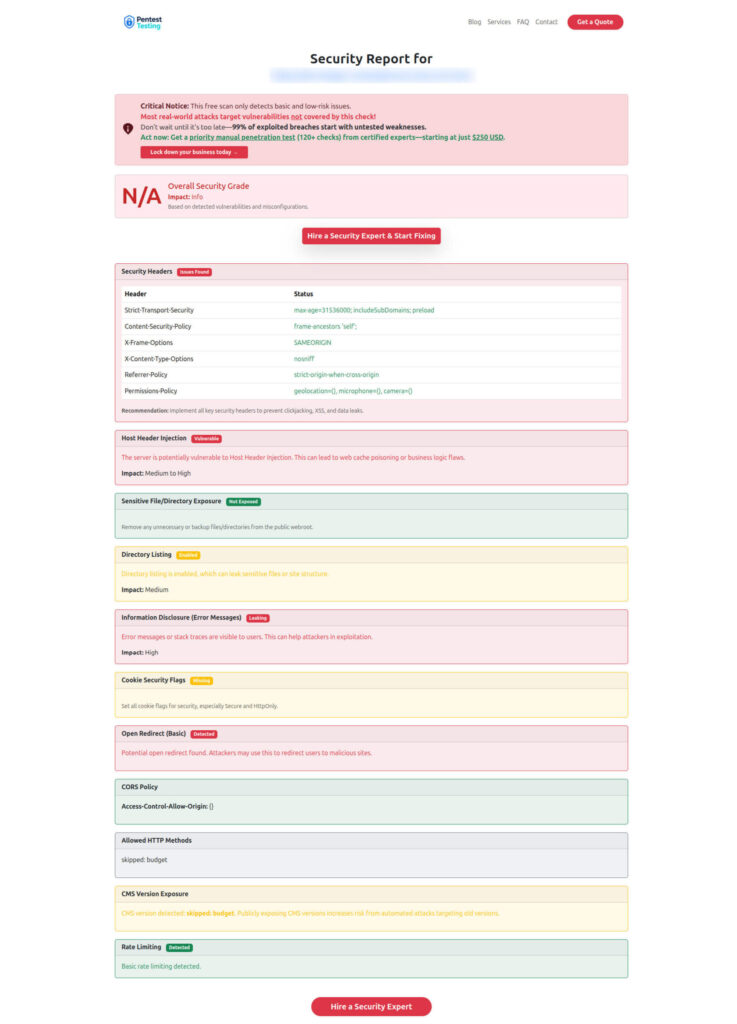
- run: echo "Remember to run the external scan and file issues using the template."Sample Scan Output from the tool to check Website Vulnerability
Implementation Checklist (copy/paste to your backlog)
- MFA enforced org-wide; WebAuthn for admins & CI; break-glass policy documented
- Secret leakage blocked via Gitleaks; all app creds short-lived via Vault/KMS; monthly rotations
- TLS locked to 1.2+/1.3, weak suites off; HSTS/CSP/XFO present; weekly evidence artifact
- Certs auto-renewed; renewal logs/artifacts kept 12+ months
- CDE segmentation IaC-as-code; default-deny; only explicit app→DB; NP/SG allow-lists
- Security gates: SAST/DAST/SCA run on PR; criticals fail; change-control file attached to PR
- External scan runs weekly via the free tool; findings are triaged to the PCI backlog with owners/SLAs
When to Phone a Friend
If your PCI scope or compensating controls feel risky, or you need a pre-QSA readiness check, talk to our team:
• PCI DSS Readiness & Advisory → pentesttesting.com/pci-dss-readiness/
• PCI DSS Remediation Services → pentesttesting.com/pci-dss-remediation-services/
We also publish hands-on playbooks for engineering leaders on the Cyber Rely Blog.
🔐 Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Find answers to commonly asked questions about PCI DSS 4.0.1 Remediation.