🛡️ Best 7 Ways to Prevent HTTP Parameter Pollution in React.js
Introduction to HTTP Parameter Pollution in React.js
As modern web applications grow in complexity, client-side frameworks like React.js become increasingly vulnerable to sophisticated attacks. One such underrated yet dangerous threat is HTTP Parameter Pollution in React.js.

This attack manipulates multiple HTTP parameters with the same name to bypass security controls or modify behaviour, often with dire consequences like data leakage, privilege escalation, or logic tampering. In this blog, we’ll walk you through how HTTP Parameter Pollution in React.js works, showcase several attack examples, and guide you through 7 best practices to detect and prevent it—backed by coding examples, vulnerability testing tools, and real-world case scenarios.
What is HTTP Parameter Pollution (HPP)?
HTTP Parameter Pollution (HPP) is a web attack technique in which attackers inject multiple parameters with the same name in HTTP requests to exploit how web applications handle them. For example:
GET /search?user=admin&user=guestDepending on how your backend or frontend parses the parameters, the outcome might favor the attacker.
💥 How HTTP Parameter Pollution Affects React.js
React apps that interact with APIs, manipulate query strings, or rely on third-party libraries like Axios, Fetch, or React Router are especially at risk. Here’s why:
- Query strings might be parsed incorrectly.
- State management may store polluted data.
- Insecure APIs might accept the wrong value.
🚨 Example Vulnerable React.js Code
import { useLocation } from 'react-router-dom';
const UserProfile = () => {
const query = new URLSearchParams(useLocation().search);
const user = query.get('user');
return <h2>Welcome, {user}</h2>;
};Attack Example:
Accessing /profile?user=admin&user=hacker might result in the app showing “Welcome, admin” but the backend processes “hacker”.
🔐 Top 7 Best Ways to Prevent HTTP Parameter Pollution in React.js
1. ✅ Always Validate Query Parameters
Use a schema validator like Yup or Zod.
import * as yup from 'yup';
const schema = yup.object().shape({
user: yup.string().required().oneOf(['admin', 'guest']),
});2. 🛡️ Use Strong URL Parsers
Avoid using URLSearchParams blindly. Instead, sanitize input values.
const getSafeQueryParam = (param) => {
const values = new URLSearchParams(window.location.search).getAll(param);
return values.length === 1 ? values[0] : null;
};3. ⚙️ Enforce Backend Rules
Your backend must reject or normalize repeated parameters.
// Example in PHP
if (is_array($_GET['user'])) {
http_response_code(400);
exit('Invalid parameter usage');
}4. 🔍 Test React Apps Using Security Tools
Automated tools like our Free Website Vulnerability Scanner can detect HPP vulnerabilities in minutes.
📸 Screenshot: Website Vulnerability Scanner Tool
Before we dive in, here’s how you can scan your React app for HTTP Parameter Pollution using our free tool.
📸 Screenshot: Sample Vulnerability Assessment Report
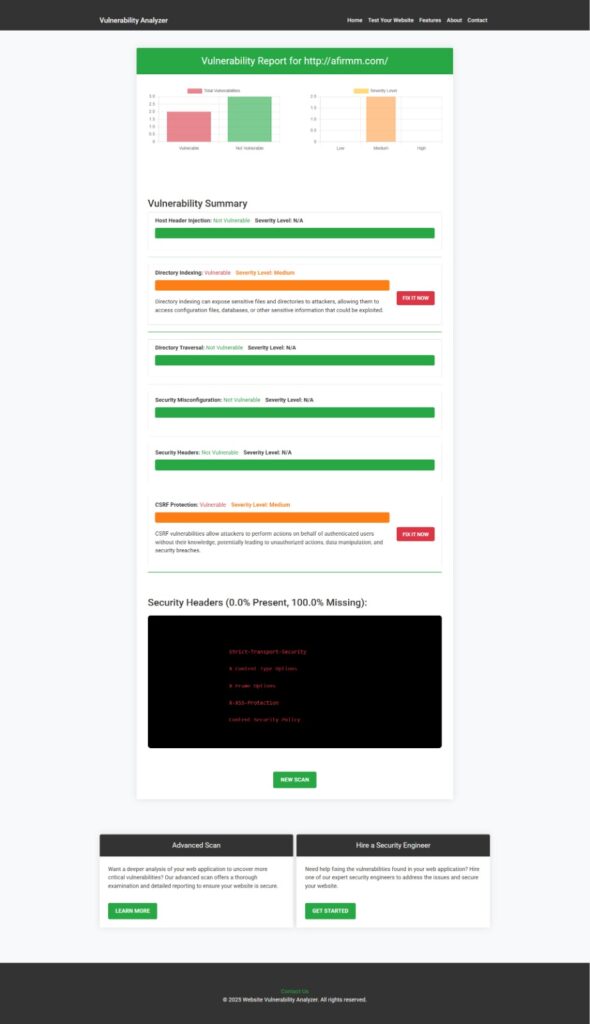
Detailed insights on vulnerabilities for developers to check Website Vulnerability.
5. 🚧 Secure Routing in React
Use exact routes and avoid passing sensitive data via query parameters.
<Route exact path="/profile" component={UserProfile} />6. 🚨 Avoid Client-Side Authorization
Never rely on the frontend to restrict user roles. It’s easily bypassed with parameter pollution.
7. 🔁 Normalize Parameters in Middleware
If using Node.js/Express for APIs:
app.use((req, res, next) => {
for (let key in req.query) {
if (Array.isArray(req.query[key])) {
req.query[key] = req.query[key][0]; // Only allow the first value
}
}
next();
});🤖 Protect AI Apps from HTTP Parameter Pollution
Are you working on AI-driven apps? Make sure they’re safe from parameter-based exploitation too. Visit our AI Application Cybersecurity Service to harden your AI models and APIs against emerging threats like HPP and prompt injection.
🔗 Related Articles You’ll Love
- Prevent LDAP Injection in React.js
- Check for Subdomain Takeover in React.js
- Define Transport Layer Security in React.js
- Prevent CORS Misconfigurations in TypeScript
- Web Cache Deception Attack in Laravel
💼 Offer Cybersecurity Services to Your Clients
Want to add penetration testing to your service stack? Check out our Partner Program and become a cybersecurity reseller today.
📬 Contact Us for Custom Penetration Testing
Need a manual code audit or deeper React.js security testing? Drop us a message on our Contact Page and we’ll assist you within 24 hours.
Final Thoughts
HTTP Parameter Pollution in React.js might not be as popular as XSS or CSRF, but it’s a silent killer when ignored. It can manipulate user roles, override sensitive parameters, or even exploit misconfigured APIs. By combining frontend validation, backend enforcement, and regular checking for Security test, you can keep your apps secure.
Want a free scan?
DM us or check 👉 https://free.pentesttesting.com/