Git CVE-2025-48384: Safe Submodules in Practice
This post is for engineers who live in Git: devs, SREs, CI owners. You’ll get the exact patched Git versions, how to check and enforce them across laptops and pipelines, plus guardrails to stop dangerous submodules from ever running code in your builds.
TL;DR
- What it is: A flaw in how Git handles CR/LF when parsing submodule paths. Crafted
.gitmodulesentries can redirect where a submodule is checked out and trigger a hook, leading to arbitrary file write → code execution on Linux/macOS. Windows not affected. - Patched Git versions:
2.43.7, 2.44.4, 2.45.4, 2.46.4, 2.47.3, 2.48.2, 2.49.1, 2.50.1. Upgrade everywhere (workstations + CI images). - KEV status: In CISA KEV, added Aug 25, 2025; due date Sept 15, 2025 for federal agencies. Treat as actively exploited.
- Biggest foot-gun:
git clone --recursivefrom untrusted sources. Don’t. Audit.gitmodulesfirst.
Explainer: CR/LF parsing → arbitrary write → RCE
NVD and the Git advisory describe a mismatch in how Git reads vs writes config values containing carriage returns. A submodule path in .gitmodules ending with \r can be interpreted differently on read, making Git check out a submodule to the wrong location. With a symlink to the hooks dir and an executable post-checkout, you can get unintended hook execution after checkout.
Datadog’s analysis shows the practical impact: a malicious repo weaponizes git clone --recursive to achieve arbitrary file write and then RCE by dropping a hook that runs on common commands (commit, merge) on Linux/macOS.
Scope: Linux/macOS are affected; Windows Git isn’t impacted in this path, per multiple vendor write-ups.
Before you merge, run a quick check on any staging/demo URLs referenced in your repo. Use our Free Website Vulnerability Scanner to catch header misconfigs and exposed files fast:
Patch window & KEV status (what to require in pipelines and laptops)
- Fix versions (install these or newer):
2.43.7, 2.44.4, 2.45.4, 2.46.4, 2.47.3, 2.48.2, 2.49.1, 2.50.1. - CISA KEV: Listed as “Git Link Following Vulnerability”, added Aug 25, 2025, with Sept 15, 2025 due date; treat as actively exploited in the wild.
- Severity: CVSS 8.1 (High) in the GitHub advisory.
Action: Pin your CI runners and dev workstations to one of the patched versions above and verify at runtime before any clone/build steps.
Quick checks for engineers
Workstations (macOS/Linux):
git --version
# require one of: 2.43.7, 2.44.4, 2.45.4, 2.46.4, 2.47.3, 2.48.2, 2.49.1, 2.50.1+Why: These are the builds that fix CVE-2025-48384.
CI images: Rebuild images with patched Git or apt/yum upgrade early in the job, then enforce with a guard step (examples below).
CI guardrails you can drop in today
1) Never auto-recursively clone untrusted submodules
Require manual review of .gitmodules before any submodule init. Block --recursive by default; prefer a two-step: clone → inspect → controlled init.
GitHub Actions: fail jobs that use --recursive from external repos
name: guard-git-recursive
on: [workflow_call, pull_request]
jobs:
block-recursive:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
steps:
- name: Detect forbidden recursive clone
run: |
set -euo pipefail
if grep -R -- '--recursive' -n .github/workflows || \
( [ -n "${GIT_TRACE:-}" ] && echo "$GIT_TRACE" | grep -- '--recursive' ); then
echo "Do not use 'git clone --recursive' from untrusted sources. Audit .gitmodules first."
exit 1
fiRationale:
--recursiveis the common exploitation path noted by researchers.
2) Audit .gitmodules before init
Create a lightweight audit that rejects suspicious paths (control chars, absolute paths, .., symlinks in target dir), and restricts protocols to https/ssh.
# scripts/audit-gitmodules.sh
set -euo pipefail
test -f .gitmodules || exit 0
# reject CR chars, absolute paths, and parent traversal
if grep -P '\r$' .gitmodules || grep -E 'path\s*=\s*/' .gitmodules || grep -E 'path\s*=\s*\.\.' .gitmodules; then
echo "Suspicious submodule paths detected in .gitmodules"; exit 1
fi
# restrict URLs to https/ssh only
if grep -E 'url\s*=\s*(git://|file://|http://)' .gitmodules; then
echo "Insecure or local protocols found in .gitmodules"; exit 1
fi
echo ".gitmodules audit passed"Add to CI before any submodule operation.
3) Disable repo-provided hooks in CI via core.hooksPath
Point hooks to an empty directory so no repository hooks can fire in CI.
mkdir -p "$HOME/.git-hooks-empty"
git config --global core.hooksPath "$HOME/.git-hooks-empty"Docs: core.hooksPath controls where Git loads hooks; using an empty dir prevents hook execution.
4) Lock down Git protocols at runtime
Forbid local/unsafe transports during clones in CI:
git -c protocol.file.allow=never -c protocol.git.allow=never clone "$REPO_URL" repo(Blocks file:// and the unauthenticated git:// transport; only https/ssh allowed.)
5) Enforce patched Git versions
GitHub Actions
- name: Enforce patched Git
run: |
set -euo pipefail
reqs="2.43.7 2.44.4 2.45.4 2.46.4 2.47.3 2.48.2 2.49.1 2.50.1"
v=$(git --version | awk '{print $3}')
ok=0
for r in $reqs; do [ "$v" = "$r" ] && ok=1; done
# allow anything > 2.50.1
[ "$(printf '%s\n2.50.1\n' "$v" | sort -V | tail -1)" = "$v" ] && ok=1
if [ $ok -ne 1 ]; then
echo "Git $v is not one of the patched versions for CVE-2025-48384."; exit 1
fiSame pattern works in GitLab CI (before_script) and Jenkins (shell step). Patched versions per NVD/GitHub.
Pre-commit checks & SBOM alerts for rogue submodules
Pre-commit (with pre-commit framework)
Add a local hook that runs the audit script whenever .gitmodules changes.
.pre-commit-config.yaml
repos:
- repo: local
hooks:
- id: audit-gitmodules
name: Audit .gitmodules for unsafe entries
entry: bash scripts/audit-gitmodules.sh
language: system
files: ^\.gitmodules$This prevents suspicious submodule definitions from landing in your main branch—long before CI. (The danger of recursive submodules in the wild is well documented around this CVE.)
SBOM-ish alerting
Most SBOM tools don’t model Git submodules as “packages,” so treat .gitmodules as a tracked artifact:
- Parse
.gitmodulesand emit each submodule URL into a small JSON alongside your SBOM. - Alert if a URL points to non-approved domains (e.g., personal forks, unknown hosts).
- Block builds if a new submodule appears without an owner approval label.
This builds on the same risk path the research highlights: unreviewed submodule URLs paired with recursive clones.
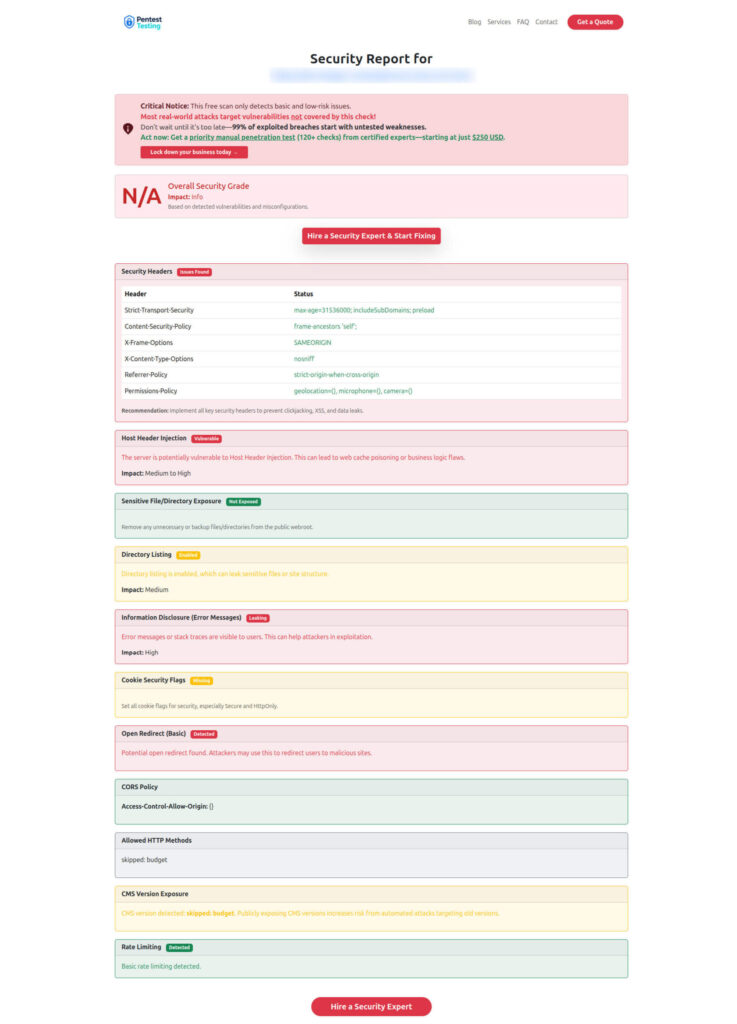
Sample vulnerability report to check Website Vulnerability, highlighting missing security headers, exposed files, and recommended remediations for a staging endpoint.
Developer hygiene checklist (copy/paste to your team)
- Upgrade Git to one of:
2.43.7/2.44.4/2.45.4/2.46.4/2.47.3/2.48.2/2.49.1/2.50.1+. - Don’t run
git clone --recursiveon unknown repos; read.gitmodulesfirst. - CI only: set
core.hooksPathto an empty dir to disable repo hooks. - Restrict protocols to
https/ssh; denyfile://andgit://. - Monitor for recursive clones and hook executions (Datadog has example detections and queries).
Sources you can share with security & management
- NVD CVE-2025-48384 (full description + fixed versions + KEV linkage). (NVD)
- GitHub advisory (GHSA-vwqx-4fm8-6qc9) (affected/patched versions, impact). (GitHub)
- CISA KEV entry (added Aug 25, 2025, due Sept 15, 2025). (CISA)
- Datadog Security Labs (how the exploit works, detections, Linux/macOS focus). (Datadog Security Labs)
- Arctic Wolf (patch day context; Windows not impacted). (Arctic Wolf)
Tie-in: scan exposed web endpoints your repos reference
Your repos’ READMEs, docs, and sample apps often link to staging or demo endpoints. After you harden Git usage, scan those endpoints with our free tool to catch header issues and exposed files quickly:
- Cyber Rely Blog — engineering-first guides you can share internally: https://www.cybersrely.com/blog/
(Related hygiene posts: Security Misconfiguration in Node.js, CVE-2025-10585: Chrome Zero-Day Patch and Sensitive Data Exposure in Node.js.) - Free Website Vulnerability Scanner — quick checks for endpoints linked from your repos: https://free.pentesttesting.com/
- Pentest Testing Corp Blog — deeper remediation playbooks: https://www.pentesttesting.com/blog/
Final word
CVE-2025-48384 is exactly the kind of bug that punishes muscle memory (--recursive) and “it worked on my machine” CI images. Patch Git everywhere, stop auto-recursive clones, and make hooks inert in CI. Do those three, and you’ll remove the sharpest edges of this class of supply-chain risk.