7 Best Fixes for Broken Access Control in Node.js
Broken Access Control in Node.js is one of the most costly, sneaky issues a team can ship. It happens when users can act beyond their permissions—reading another tenant’s data, editing foreign records, downloading restricted files, or elevating roles. In this guide, we’ll demystify Broken Access Control in Node.js with clear patterns, many copy-paste code examples, and a deployment-ready checklist. You’ll learn how to stop IDORs, enforce RBAC/ABAC, secure file routes, and test your defenses.
What Broken Access Control in Node.js Looks Like
- IDOR (Insecure Direct Object Reference):
/api/users/1234returns data to a user who isn’t1234. - Missing resource ownership checks: Authenticated ≠ authorized.
- Over-permissive routes: Wildcard routes or admin endpoints without guards.
- Leaky files & buckets: Direct URLs to sensitive files, predictable keys, unsafe path joins.
- Privilege escalation: Users changing their own role/team/org fields.
- Multi-tenant drift: Tenant filter missing from queries.
Why Broken Access Control in Node.js Happens
Broken Access Control in Node.js often stems from mixing authentication (who you are) with authorization (what you can do). Express/Nest apps commonly authenticate via cookies or JWTs but forget to check resource ownership, role permissions, or tenant isolation per request. Files and admin routes are especially prone to drift.
The 7 Best Fixes (with Copy-Paste Code)
1) Centralize AuthZ: One Guard to Rule Them All (RBAC)
Create a single authorization middleware that checks roles and scopes consistently.
// authz.js
export const requireAuth = (req, res, next) => {
if (!req.user) return res.sendStatus(401);
next();
};
export const allowRoles = (...roles) => (req, res, next) => {
if (!req.user) return res.sendStatus(401);
if (!roles.includes(req.user.role)) return res.sendStatus(403);
next();
};
// example user payload decoded from JWT/cookie: { id, role, tenantId, scopes: [...] }// routes.js (Express)
import express from "express";
import { requireAuth, allowRoles } from "./authz.js";
const router = express.Router();
router.get("/admin/metrics",
requireAuth,
allowRoles("admin"),
(req, res) => res.json({ ok: true })
);
export default router;Pro tip: Include scopes for fine-grained control (e.g., invoice:read, invoice:write) and check both role and scope.
2) Always Check Resource Ownership (Stop IDORs)
Even with roles, verify the resource belongs to the current user or tenant.
// posts.controller.js (Mongoose)
import Post from "./models/Post.js";
// GET /api/posts/:id
export const getPost = async (req, res) => {
const { id } = req.params;
const post = await Post.findOne({ _id: id, ownerId: req.user.id }); // ownership check!
if (!post) return res.sendStatus(404);
res.json(post);
};// With SQL/Prisma (PostgreSQL)
const post = await prisma.post.findFirst({
where: { id: req.params.id, ownerId: req.user.id }
});
if (!post) return res.status(404).end();This pattern crushes Broken Access Control in Node.js by denying cross-user reads even if IDs are guessed.
Screenshot of our free Website Vulnerability Scanner homepage
3) Deny by Default + Route-Level Guards
Place authz checks closest to the resource—don’t rely on “we checked it earlier.”
// A reusable guard that pairs with scopes
export const requireScope = (...scopes) => (req, res, next) => {
if (!req.user) return res.sendStatus(401);
if (!req.user.scopes) return res.sendStatus(403);
const ok = scopes.every(s => req.user.scopes.includes(s));
return ok ? next() : res.sendStatus(403);
};
// Example: only allow writing if both role and scope match
router.post("/api/tickets",
requireAuth,
allowRoles("agent", "admin"),
requireScope("ticket:create"),
async (req, res) => {
// create logic
res.status(201).json({ ok: true });
}
);4) Hide & Validate Identifiers (No Predictable IDs)
Use UUIDs/ULIDs, never trust client-provided owner IDs, and double-check tenant filters.
// Tenant isolation middleware
export const withTenant = (req, res, next) => {
if (!req.user?.tenantId) return res.sendStatus(401);
req.tenantId = req.user.tenantId;
next();
};
router.get("/api/invoices/:invoiceId",
requireAuth,
withTenant,
async (req, res) => {
const invoice = await prisma.invoice.findFirst({
where: { id: req.params.invoiceId, tenantId: req.tenantId }
});
if (!invoice) return res.sendStatus(404);
res.json(invoice);
}
);This is essential if you want to avoid multi-tenant Broken Access Control in Node.js.
5) ABAC with Context (When RBAC Isn’t Enough)
Attribute-Based Access Control checks who, what, and context (time, status, ownership).
// abac.js - tiny example
export function canEditOrder(user, order) {
if (!user || !order) return false;
const isOwner = order.customerId === user.id;
const isAdmin = user.role === "admin";
const editableStatuses = ["DRAFT", "PENDING"];
return (isOwner && editableStatuses.includes(order.status)) || isAdmin;
}
// usage
router.patch("/api/orders/:id",
requireAuth,
async (req, res) => {
const order = await prisma.order.findUnique({ where: { id: req.params.id } });
if (!order) return res.sendStatus(404);
if (!canEditOrder(req.user, order)) return res.sendStatus(403);
// ...apply updates...
res.json({ ok: true });
}
);6) Lock Down Files, Paths, and Downloads
Prevent path traversal and ensure file ownership/visibility.
import path from "node:path";
import fs from "node:fs/promises";
const BASE = path.resolve("/srv/app/uploads");
router.get("/download/:fileId",
requireAuth,
async (req, res) => {
const file = await prisma.file.findFirst({
where: { id: req.params.fileId, ownerId: req.user.id } // check ownership
});
if (!file) return res.sendStatus(404);
const full = path.resolve(BASE, file.storageName);
if (!full.startsWith(BASE)) return res.sendStatus(403); // block traversal
try {
await fs.access(full);
res.download(full, file.originalName);
} catch {
res.sendStatus(404);
}
}
);For cloud storage, generate short-lived, scoped pre-signed URLs server-side after the same checks.
7) Test Your Access Rules (Automate the Guardrails)
Write tests that prove “user A can’t see user B’s stuff.”
// __tests__/access.spec.js (Jest + Supertest)
import request from "supertest";
import app from "../app.js";
test("user cannot read another user's invoice", async () => {
const tokenA = await loginAs("[email protected]");
const invoiceB = "uuid-of-bobs-invoice";
const res = await request(app)
.get(`/api/invoices/${invoiceB}`)
.set("Authorization", `Bearer ${tokenA}`);
expect(res.status).toBe(404); // conceal existence
});This closes the loop on Broken Access Control in Node.js by preventing regressions.
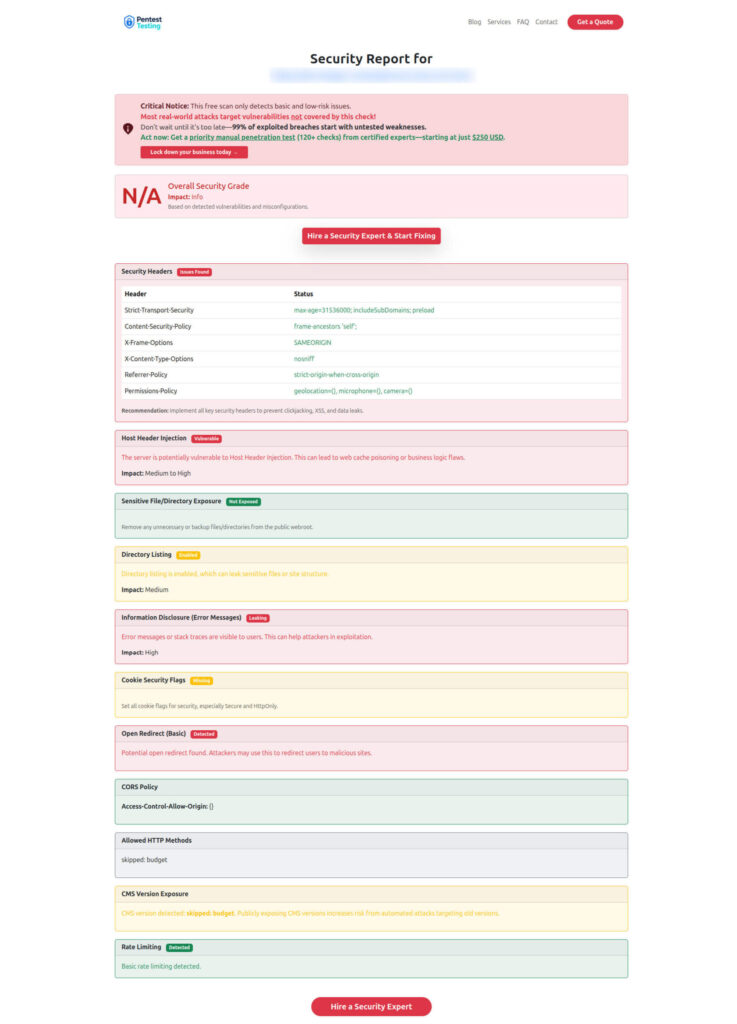
Sample Assessment Report generated by our tool to check Website Vulnerability
More Practical Code Patterns
Enforce Server-Side Filtering (No “client decides”)
// Never accept ownerId/tenantId from the client
const data = req.body;
delete data.ownerId;
delete data.tenantId;
const created = await prisma.note.create({
data: { ...data, ownerId: req.user.id, tenantId: req.user.tenantId }
});Prevent Role/Org Tampering
// block forbidden updates
const forbidden = ["role", "tenantId", "isAdmin"];
for (const k of forbidden) delete req.body[k];NestJS Guard (Role + Scope)
// roles.guard.ts
import { CanActivate, ExecutionContext, Injectable } from '@nestjs/common';
@Injectable()
export class RolesGuard implements CanActivate {
constructor(private roles: string[] = []) {}
canActivate(ctx: ExecutionContext) {
const req = ctx.switchToHttp().getRequest();
return !!req.user && this.roles.includes(req.user.role);
}
}
// usage
@UseGuards(new RolesGuard(['admin']))
@Get('admin/metrics')
getMetrics() { /* ... */ }GraphQL Resolver Check
// resolvers.js
const resolvers = {
Query: {
order: async (_, { id }, { user, prisma }) => {
if (!user) throw new Error("Unauthorized");
const order = await prisma.order.findFirst({ where: { id, customerId: user.id } });
if (!order) throw new Error("Not found");
return order;
}
}
};CORS Isn’t AuthZ (But Don’t Make It Worse)
Lock CORS to known origins and don’t leak cookies cross-site:
import cors from "cors";
app.use(cors({
origin: ["https://app.example.com"],
credentials: true,
methods: ["GET","POST","PATCH","DELETE"]
}));Quick Checklist (Ship This)
- Every protected route uses
requireAuthand a role/scope guard - Ownership or tenant filter for reads & writes
- IDs are UUID/ULID; server sets owner/tenant fields
- Admin endpoints isolated; deny by default
- File downloads validate ownership & normalize paths
- Tests cover cross-user/tenant access
- Least-privilege roles; remove unsafe “god” scopes
- Short-lived pre-signed URLs for object storage
Related Reading (from CyberSrely)
- Security Misconfiguration in Node.js — https://www.cybersrely.com/security-misconfiguration-in-node-js/
- SQL Injection Attack Mitigation in Node.js — https://www.cybersrely.com/sql-injection-attack-mitigation-in-node-js/
- SQLi Prevention in React.js — https://www.cybersrely.com/sqli-prevention-in-react-js/
- Git CVE-2025-48384: Safe Submodules in Practice — https://www.cybersrely.com/git-cve-2025-48384/
Also see our guide on network threats: Prevent MITM Attack in WordPress — https://www.pentesttesting.com/prevent-mitm-attack-in-wordpress/
How We Can Help (Services & Compliance Backlinks)
Managed IT & AppSec
Strengthen operations while we harden your app’s access control layers.
Managed IT Services — https://www.pentesttesting.com/managed-it-services/
AI Application Cybersecurity
Secure LLM features and AI microservices with authz policies that include model context and data lineage.
AI Application Cybersecurity — https://www.pentesttesting.com/ai-application-cybersecurity/
White-Label Security for Agencies
Offer your clients audits, remediation, and ongoing testing under your brand.
Offer Cybersecurity Service to Your Client — https://www.pentesttesting.com/offer-cybersecurity-service-to-your-client/
Compliance & Risk Management
Map your access controls to frameworks like HIPAA, PCI DSS, SOC 2, ISO 27001, GDPR and close gaps fast.
- Risk Assessment Services — https://www.pentesttesting.com/risk-assessment-services/
- Remediation Services — https://www.pentesttesting.com/remediation-services/
Try This Now (Free Scan)
Run our free website vulnerability scanner: https://free.pentesttesting.com/
It flags patterns that often lead to Broken Access Control in Node.js and gives you a prioritized report.
Conclusion
If you remember one thing, let it be this: every route needs explicit authorization. With centralized guards, ownership checks, and tests that try to break your app, you can eliminate Broken Access Control in Node.js before attackers find it.
🔐 Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Find answers to commonly asked questions about Broken Access Control in Node.js.