CSRF Prevention in Node.js — A Practical, Copy-Ready Guide
Cross-Site Request Forgery (CSRF) is still one of the most reliable ways attackers trick browsers into performing actions the user never intended—like changing a password, transferring funds, or deleting data. In this long-form, code-rich guide, we’ll show the 10 Best CSRF Prevention in Node.js techniques you can apply right now. We’ll mix CSRF Prevention in Node.js best practices, Express middleware snippets, SameSite cookies, Origin/Referer validation, double-submit cookies, and examples for SPAs (React/Vue) and server-rendered apps (EJS/Pug).

You’ll also find two embedded screenshots: one of our free website security tools page and one of a vulnerability assessment report generated by our scanner. And if you want to go deeper into related topics, we’ve linked to our previous posts and service pages.
What is CSRF (in one minute)?
- CSRF forces a victim’s browser to send an authenticated request to your app without the victim’s intention.
- It typically abuses cookie-based authentication (session or JWT in cookies).
- Symptoms: Account changes, unwanted admin actions, or “mystery” POST/PUT/DELETE requests.
TL;DR: The 10 Best Techniques (Checklist)
- Use CSRF tokens on state-changing requests.
- Set cookies with
SameSite=LaxorStrict+Secure+HttpOnly. - Enforce Origin/Referer checks for sensitive routes.
- Use the double-submit cookie pattern if tokens via session aren’t feasible.
- Lock down CORS and block credentialed requests from untrusted origins.
- For SPAs, propagate a token via meta tag or header and send with each write request.
- Rotate session IDs after login and critical steps.
- Deny JSON CSRF by enforcing content types (e.g., JSON + custom headers).
- Apply defense-in-depth with Helmet and route-level guards.
- Test: automated checks that 403 is returned when tokens/headers are missing or invalid.
We’ll now implement each step-by-step CSRF Prevention tips.
1) CSRF Tokens with csurf (Express)
The csurf middleware is a battle-tested way to implement CSRF Prevention in Node.js using synchronizer tokens.
npm i express cookie-parser express-session csurf helmetSession-based tokens
// app.js (CommonJS)
const express = require('express');
const session = require('express-session');
const cookieParser = require('cookie-parser');
const csrf = require('csurf');
const helmet = require('helmet');
const app = express();
app.use(helmet());
// Parse cookies and bodies
app.use(cookieParser());
app.use(express.urlencoded({ extended: true }));
app.use(express.json());
// Session (for server-side token storage)
app.use(session({
secret: process.env.SESSION_SECRET || 'supersecret',
resave: false,
saveUninitialized: false,
cookie: {
httpOnly: true, // JS can’t read
sameSite: 'lax', // mitigate CSRF by default
secure: true // set true behind HTTPS
}
}));
// CSRF middleware (session-based)
app.use(csrf());
// Expose token to templates/SPAs
app.use((req, res, next) => {
res.locals.csrfToken = req.csrfToken();
next();
});
app.get('/form', (req, res) => {
// e.g., render EJS and include res.locals.csrfToken
res.send(`
<form action="/change-email" method="POST">
<input type="hidden" name="_csrf" value="${res.locals.csrfToken}">
<input type="email" name="email" placeholder="New email"/>
<button>Update</button>
</form>
`);
});
app.post('/change-email', (req, res) => {
// If token fails, csurf throws, typically 403
res.json({ ok: true });
});
app.listen(3000);Cookie-based tokens (no server session)
// Cookie-based tokens (note: csurf supports cookie mode)
app.use(csrf({
cookie: {
httpOnly: true,
sameSite: 'lax',
secure: true
}
}));Why it works: Every state-changing request carries a token the attacker cannot read from the victim’s browser (thanks to HttpOnly cookies or server session binding). This is the core of CSRF Prevention in Node.js.
2) SameSite, Secure, and HttpOnly Cookies (Must-Do)
app.use(session({
secret: process.env.SESSION_SECRET || 'supersecret',
cookie: {
httpOnly: true,
sameSite: 'lax', // 'strict' for highly sensitive flows
secure: true // ensure HTTPS
}
}));- SameSite=Lax blocks most cross-site POSTs automatically while keeping usability (e.g., normal link navigation).
- Strict is stronger but can break legitimate cross-site flows.
- Secure ensures cookies only travel over HTTPS.
3) Validate Origin / Referer on Sensitive Routes
Even with tokens, add a second gate: only accept writes from your own origin.
const TRUSTED_ORIGINS = new Set([
'https://app.example.com',
'https://admin.example.com'
]);
function originGuard(req, res, next) {
if (['GET', 'HEAD', 'OPTIONS'].includes(req.method)) return next();
const origin = req.headers.origin;
const referer = req.headers.referer;
const passes =
(origin && TRUSTED_ORIGINS.has(origin)) ||
(referer && [...TRUSTED_ORIGINS].some(o => referer.startsWith(o)));
if (!passes) return res.status(403).json({ error: 'Untrusted origin' });
next();
}
app.use(originGuard);This provides defense-in-depth for CSRF Prevention in Node.js.
4) Double-Submit Cookie Pattern (When Sessions Aren’t Practical)
If you can’t or won’t use sessions, you can set a CSRF cookie (readable by JS) and also send it in a header. The server compares them.
Server: set and verify
const crypto = require('crypto');
app.get('/csrf-token', (req, res) => {
const token = crypto.randomBytes(32).toString('hex');
// JS-readable cookie on purpose here
res.cookie('XSRF-TOKEN', token, {
sameSite: 'lax',
secure: true
});
res.json({ token }); // SPA can store in memory or <meta>
});
function doubleSubmitGuard(req, res, next) {
if (['GET', 'HEAD', 'OPTIONS'].includes(req.method)) return next();
const cookieToken = req.cookies['XSRF-TOKEN'];
const headerToken = req.get('X-CSRF-Token');
if (!cookieToken || !headerToken || cookieToken !== headerToken) {
return res.status(403).json({ error: 'Invalid CSRF token' });
}
next();
}
app.use(doubleSubmitGuard);Client (fetch/axios)
// Example with Axios (browser)
import axios from 'axios';
// Retrieve token at app load (or from <meta>)
const { data } = await axios.get('/csrf-token', { withCredentials: true });
axios.defaults.headers.common['X-CSRF-Token'] = data.token;
axios.defaults.withCredentials = true; // send cookies too
// Now any POST will include header and cookie
await axios.post('/api/profile', { name: 'Alice' });5) Lock Down CORS for Credentialed Requests
If your app uses cookies across origins, CORS Prevention must be precise.
const cors = require('cors');
app.use(cors({
origin: ['https://app.example.com'],
credentials: true,
methods: ['GET','POST','PUT','PATCH','DELETE'],
allowedHeaders: ['Content-Type', 'X-CSRF-Token']
}));Avoid origin: true or * when credentials: true is in play. Tighter CORS directly supports CSRF Prevention in Node.js by restricting where credentialed requests can originate.
6) SPA + Server Render Patterns (Real-World)
EJS (server rendered form)
<!-- views/settings.ejs -->
<form action="/settings" method="POST">
<input type="hidden" name="_csrf" value="<%= csrfToken %>">
<input type="text" name="displayName" />
<button>Save</button>
</form>SPA (meta tag + header)
<!-- Inject at layout render -->
<meta name="csrf-token" content="<%= csrfToken %>" />// Read token and set on requests
const token = document.querySelector('meta[name="csrf-token"]').content;
fetch('/api/settings', {
method: 'POST',
headers: {
'Content-Type': 'application/json',
'X-CSRF-Token': token
},
body: JSON.stringify({ displayName: 'Alice' }),
credentials: 'include'
});7) Block JSON CSRF & Enforce Content Types
Some CSRF attacks abuse permissive content types or legacy form behaviors. Enforce strict JSON and a custom header:
function jsonOnly(req, res, next) {
if (['POST','PUT','PATCH','DELETE'].includes(req.method)) {
const ct = (req.headers['content-type'] || '').toLowerCase();
if (!ct.startsWith('application/json')) {
return res.status(415).json({ error: 'JSON required' });
}
if (!req.get('X-CSRF-Token')) {
return res.status(403).json({ error: 'Missing X-CSRF-Token' });
}
}
next();
}
app.use(jsonOnly);8) Session Rotation After Login
app.post('/login', (req, res, next) => {
// ...verify user...
req.session.regenerate(err => {
if (err) return next(err);
req.session.userId = user.id;
res.json({ ok: true });
});
});Rotation prevents session fixation and reduces the window for CSRF token theft.
9) Add Helmet and Route-Level Guards
app.use(require('helmet')({
// Defaults are good; you can also tune:
crossOriginOpenerPolicy: { policy: 'same-origin' }
}));
// Combine with originGuard, jsonOnly, csurf/doubleSubmitGuard, etc.Layered controls are the philosophy of CSRF Prevention in Node.js.
10) Test Your CSRF Controls
npm i -D supertest jest// csrf.test.js
const request = require('supertest');
const app = require('./app');
test('POST without token is blocked', async () => {
await request(app).post('/change-email')
.send({ email: '[email protected]' })
.expect(403);
});
test('POST with token succeeds', async () => {
const agent = request.agent(app);
const resForm = await agent.get('/form').expect(200);
const token = /name="_csrf" value="([^"]+)"/.exec(resForm.text)[1];
await agent.post('/change-email')
.set('Content-Type', 'application/x-www-form-urlencoded')
.send(`_csrf=${token}&[email protected]`)
.expect(200);
});Automated tests ensure your CSRF Prevention in Node.js remains intact as code evolves.
See It in Action — Our Free Security Tools
Below is where we showcase two screenshots inside the content (not at the end):
Explore our free Website Vulnerability Scanner and quick checks to harden your apps:
A real report to check Website Vulnerability, highlighting risky endpoints and missing CSRF defenses:
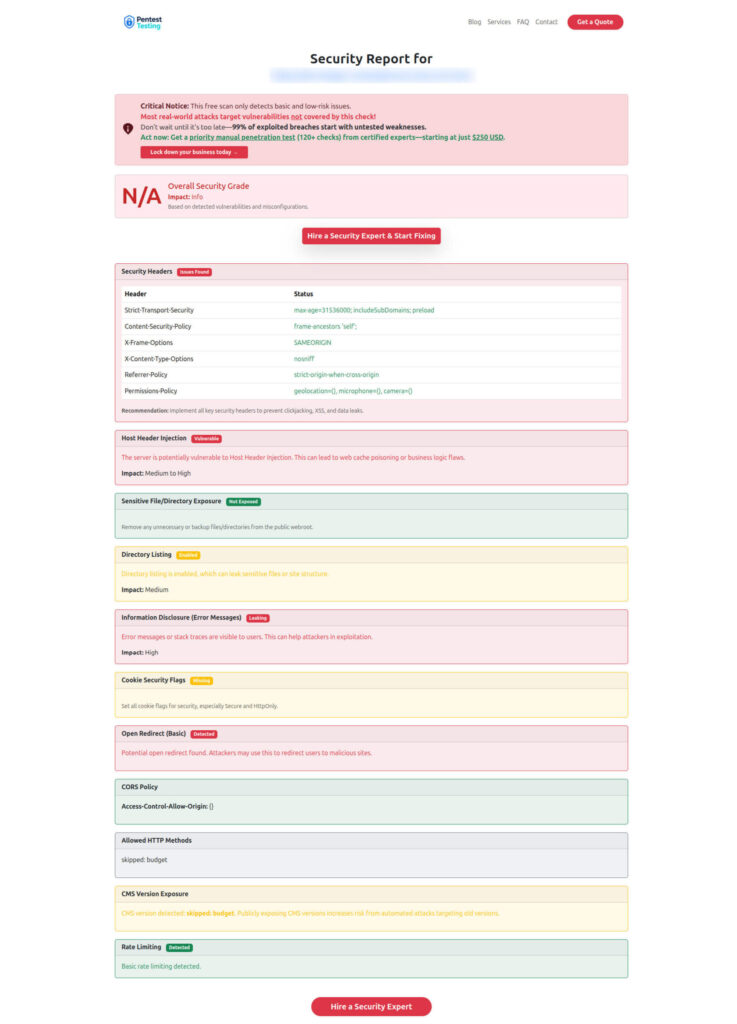
Tip: Run your app’s staging URL in our scanner right after you implement the techniques in this CSRF Prevention in Node.js guide.
Related Reading & Internal Linking
- Deep dive into path issues: Directory Traversal Attack in WordPress
https://www.pentesttesting.com/directory-traversal-attack-in-wordpress/ - Previous posts on Cybersrely you may love:
- XSS Prevention in Node.js — https://www.cybersrely.com/xss-prevention-in-node-js/
- Fix IDOR Vulnerability in Node.js — https://www.cybersrely.com/fix-idor-vulnerability-in-node-js/
- Prevent XML Injection in React.js — https://www.cybersrely.com/prevent-xml-injection-in-react-js/
- Prevent XML Injection in TypeScript — https://www.cybersrely.com/prevent-xml-injection-in-typescript/
These articles complement CSRF Prevention in Node.js by covering adjacent threats like XSS and XML injection.
Services That Help You Go Faster (Backlinks & CTAs)
Managed IT Services (Pentest Testing Corp.)
From patching to incident response pipelines, we help teams ship securely.
https://www.pentesttesting.com/managed-it-services/
AI Application Cybersecurity
Secure LLM apps, prompt pipelines, and vector stores—end-to-end.
https://www.pentesttesting.com/ai-application-cybersecurity/
Offer Cybersecurity Service to Your Client
Agencies and MSPs: white-label security services with our team.
https://www.pentesttesting.com/offer-cybersecurity-service-to-your-client/
Talk to Us
Have questions about CSRF Prevention in Node.js or anything AppSec?
https://www.cybersrely.com/contact-us/
Putting It All Together (Comprehensive Example)
// secure-app.js
const express = require('express');
const session = require('express-session');
const cookieParser = require('cookie-parser');
const csrf = require('csurf');
const helmet = require('helmet');
const cors = require('cors');
const TRUSTED_ORIGINS = new Set(['https://app.example.com']);
const app = express();
app.use(helmet());
app.use(cookieParser());
app.use(express.json());
app.use(express.urlencoded({ extended: true }));
app.use(session({
secret: process.env.SESSION_SECRET || 'supersecret',
resave: false,
saveUninitialized: false,
cookie: { httpOnly: true, sameSite: 'lax', secure: true }
}));
app.use(cors({
origin: [...TRUSTED_ORIGINS],
credentials: true,
methods: ['GET','POST','PUT','PATCH','DELETE'],
allowedHeaders: ['Content-Type', 'X-CSRF-Token']
}));
function originGuard(req, res, next) {
if (['GET','HEAD','OPTIONS'].includes(req.method)) return next();
const origin = req.headers.origin;
const referer = req.headers.referer || '';
const pass = (origin && TRUSTED_ORIGINS.has(origin)) ||
[...TRUSTED_ORIGINS].some(o => referer.startsWith(o));
if (!pass) return res.status(403).json({ error: 'Untrusted origin' });
next();
}
app.use(originGuard);
function jsonOnly(req, res, next) {
if (!['POST','PUT','PATCH','DELETE'].includes(req.method)) return next();
const ct = (req.headers['content-type'] || '').toLowerCase();
if (!ct.startsWith('application/json')) {
return res.status(415).json({ error: 'JSON required' });
}
next();
}
app.use(jsonOnly);
// CSRF (session-based token)
app.use(csrf());
// Expose token to views/SPAs
app.get('/csrf-token', (req, res) => {
res.json({ token: req.csrfToken() });
});
app.post('/profile', (req, res) => {
// protected route; token checked by csurf
res.json({ saved: true });
});
app.post('/login', (req, res, next) => {
// ...authenticate...
req.session.regenerate(err => {
if (err) return next(err);
req.session.userId = '123';
res.json({ ok: true });
});
});
app.listen(3000);Client side (SPA)
// Retrieve and attach CSRF token
const tokenRes = await fetch('/csrf-token', { credentials: 'include' });
const { token } = await tokenRes.json();
await fetch('/profile', {
method: 'POST',
headers: { 'Content-Type': 'application/json', 'X-CSRF-Token': token },
credentials: 'include',
body: JSON.stringify({ nickname: 'cybersrely-fan' })
});This composite setup embodies layered CSRF Prevention in Node.js with strong defaults and minimal developer friction.
Common Pitfalls to Avoid
- Relying only on SameSite: helpful but not complete. Use tokens and origin checks.
- Wildcard CORS with credentials: invites CSRF. Always whitelist.
- Sending tokens in URLs: they leak in logs and Referer headers.
- Forgetting non-form endpoints: CSRF hits any state-changing method, not only HTML forms.
- Not testing failures: always assert that missing/invalid tokens yield 403.
Final Note
If you implement even half of these Best CSRF Prevention in Node.js practices this week, you’ll massively reduce real-world risk. When you’re ready for a deeper assessment, scan your site with our free tool for a Website Security check (screenshots above) and reach out via our Contact Us page.
🔐 Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Find answers to commonly asked questions about CSRF Prevention in Node.js.
Pingback: Fix IDOR Vulnerability in Node.js with 10 Best Ways