Weak API Authentication in React.js — 10 Best Fixes with Real Code
Weak API Authentication in React.js is one of the fastest ways attackers pivot from a harmless UI to full data exfiltration. In this guide, we’ll unpack what “Weak API Authentication in React.js” actually looks like, how it gets exploited, and 10 best fixes you can apply today—complete with React code you can paste into your project.

We’ll also show you how to validate your fixes using our free scanner and link to deeper reads and service pages.
Why “Weak API Authentication in React.js” happens
Modern React apps often rely on token-based auth to talk to microservices. Weak API Authentication in React.js typically stems from:
- Storing long-lived tokens in
localStorageorsessionStorage. - Shipping tokens over HTTP (no TLS) or in query strings.
- Missing CSRF defenses when using cookie-based sessions.
- Skipping refresh-token rotation and revocation.
- Over-permissive CORS and missing audience/issuer checks.
- Leaking secrets in source or build artifacts.
Each mistake opens the door to session theft, replay, or privilege escalation—classic symptoms of Weak API Authentication.
Insecure patterns (recognize & remove)
1) Hardcoding tokens or using localStorage
// ❌ Insecure: token in localStorage is accessible to XSS
const token = localStorage.getItem('access_token');
fetch('https://api.example.com/profile', {
headers: { Authorization: `Bearer ${token}` }
}).then(r => r.json()).then(console.log);2) Sending tokens in query strings
// ❌ Insecure: tokens in URLs end up in logs
fetch(`https://api.example.com/profile?token=${token}`);3) No CSRF when using cookies
// ❌ Insecure: sending credentials but no CSRF token
fetch('https://api.example.com/settings', {
method: 'POST',
credentials: 'include',
body: JSON.stringify({ theme: 'dark' })
});4) Over-permissive CORS
// ❌ Server allowing '*', methods and headers wide open (example)
app.use(cors({ origin: '*', credentials: true })); // Dangerous comboThese anti-patterns are the backbone of Weak API Authentication in React.js exploits.
Quick visual: verify your setup (free tool)
Screenshot of our Website Vulnerability Scanner tool Webpage
10 Best fixes (with copy-paste React/JS code)
1) Prefer httpOnly, Secure cookies over localStorage
Keep access tokens out of JS reach. Store only short-lived access tokens server-side (session or cookie) and use httpOnly + Secure + SameSite.
Server (Express) example:
// Set a short-lived httpOnly cookie
res.cookie('sid', sessionId, {
httpOnly: true,
secure: true, // HTTPS only
sameSite: 'lax', // or 'strict' if UX allows
maxAge: 1000 * 60 * 10
});Client (React) example:
// Include credentials so browser sends the cookie
await fetch('/api/me', { credentials: 'include' });This design drastically reduces Weak API Authentication risks from XSS token theft.
2) Add CSRF protection for cookie sessions
Use a double-submit token or synchronizer pattern.
Server sets CSRF token (readable by JS) and session cookie (httpOnly):
res.cookie('csrf', csrfToken, { sameSite: 'lax', secure: true });
res.cookie('sid', sid, { httpOnly: true, sameSite: 'lax', secure: true });React adds CSRF header:
function getCookie(name) {
return document.cookie.split('; ')
.find(r => r.startsWith(name+'='))?.split('=')[1];
}
await fetch('/api/settings', {
method: 'POST',
credentials: 'include',
headers: {
'Content-Type': 'application/json',
'X-CSRF-Token': getCookie('csrf')
},
body: JSON.stringify({ theme: 'dark' })
});3) Use OAuth2/OIDC with PKCE (avoid implicit flow)
PKCE removes the need for a client secret in the SPA.
Generate code verifier & challenge (React/JS):
const makeRandom = len => btoa(String.fromCharCode(...crypto.getRandomValues(new Uint8Array(len))))
.replace(/[^a-zA-Z0-9]/g,'').slice(0, len);
const toBase64Url = buf => btoa(String.fromCharCode(...new Uint8Array(buf)))
.replace(/\+/g,'-').replace(/\//g,'_').replace(/=+$/,'');
async function pkceChallenge(verifier) {
const data = new TextEncoder().encode(verifier);
const digest = await crypto.subtle.digest('SHA-256', data);
return toBase64Url(digest);
}
const verifier = makeRandom(64);
const challenge = await pkceChallenge(verifier);
// Save verifier in memory (not localStorage) until callback
sessionStorage.setItem('pkce_verifier', verifier);
location.href = `https://idp.example.com/authorize?client_id=...&response_type=code&code_challenge=${challenge}&code_challenge_method=S256&redirect_uri=${encodeURIComponent(location.origin + '/callback')}&scope=openid%20profile%20email&state=xyz`;Callback exchanges code (server or trusted backend) for tokens, then issues short-lived cookies.
4) Rotate refresh tokens, handle 401s centrally
Use Axios interceptors to auto-refresh once and retry.
import axios from 'axios';
const api = axios.create({ baseURL: '/api', withCredentials: true });
let refreshing = null;
api.interceptors.response.use(
r => r,
async err => {
if (err.response?.status !== 401 || refreshing) throw err;
try {
refreshing = api.post('/auth/refresh'); // refresh rotates refresh token on server
await refreshing;
refreshing = null;
return api(err.config); // retry original
} catch (e) {
refreshing = null;
// redirect to login
window.location.href = '/login';
throw e;
}
}
);5) Bind tokens to the client (DPoP / PoP concept)
Proof-of-possession reduces replay. Example header creation:
// Minimal DPoP-like header demo (conceptual)
async function dpopHeader(url, method, keyPair) {
const now = Math.floor(Date.now() / 1000);
const jwtPayload = { htu: url, htm: method, iat: now, jti: crypto.randomUUID() };
// Sign jwtPayload with keyPair.privateKey via WebCrypto → produce JWS
// Send 'DPoP: <JWS>' with the request; server verifies
}Even a lightweight PoP scheme weakens Weak API Authentication in React.js attack paths.
6) Strict CORS (no wildcards with credentials)
When credentials: 'include', never use *.
app.use(cors({
origin: ['https://app.example.com'], // exact origins only
credentials: true,
methods: ['GET','POST','PUT','DELETE'],
allowedHeaders: ['Content-Type','X-CSRF-Token','Authorization']
}));7) Limit scopes and audiences
Request only what you need; verify audience (aud) and issuer (iss) on the server.
// Example client requesting minimal scope
location.href = `...&scope=openid%20profile&audience=api.example.com`;8) Keep tokens out of logs & URLs
Prefer headers; sanitize logging.
await fetch('/api/transfer', {
method: 'POST',
headers: { 'Authorization': `Bearer ${accessToken}` }, // never in URL
body: JSON.stringify({ amount: 100 })
});9) Short lifetimes + idle timeout
Short access token TTLs with server-enforced idle timeouts shrink the window for abuse.
// Server pseudo-config
const ACCESS_TTL = 600; // 10 minutes
const IDLE_TIMEOUT = 900; // 15 minutes10) Harden error handling & telemetry
Return generic auth errors; track anomalies (geo-velocity, unusual UAs) and lock compromised sessions.
try {
const res = await api.get('/me');
// ...
} catch (e) {
// Avoid leaking “token expired vs user not found”
console.error('Auth failed');
}A secure React AuthProvider (end-to-end pattern)
import React, { createContext, useEffect, useState, useContext } from 'react';
import axios from 'axios';
const AuthCtx = createContext(null);
const api = axios.create({ baseURL: '/api', withCredentials: true });
export function AuthProvider({ children }) {
const [user, setUser] = useState(null);
const [ready, setReady] = useState(false);
api.interceptors.response.use(
r => r,
async err => {
if (err.response?.status !== 401) throw err;
try {
await api.post('/auth/refresh');
return api(err.config);
} catch {
setUser(null);
window.location.href = '/login';
throw err;
}
}
);
useEffect(() => {
(async () => {
try {
const { data } = await api.get('/me');
setUser(data);
} catch {}
setReady(true);
})();
}, []);
const logout = async () => {
await api.post('/auth/logout');
setUser(null);
};
return (
<AuthCtx.Provider value={{ user, ready, logout }}>
{children}
</AuthCtx.Provider>
);
}
export const useAuth = () => useContext(AuthCtx);This pattern avoids Weak API Authentication in React.js by centering refresh rotation, cookie transport, and consistent error handling.
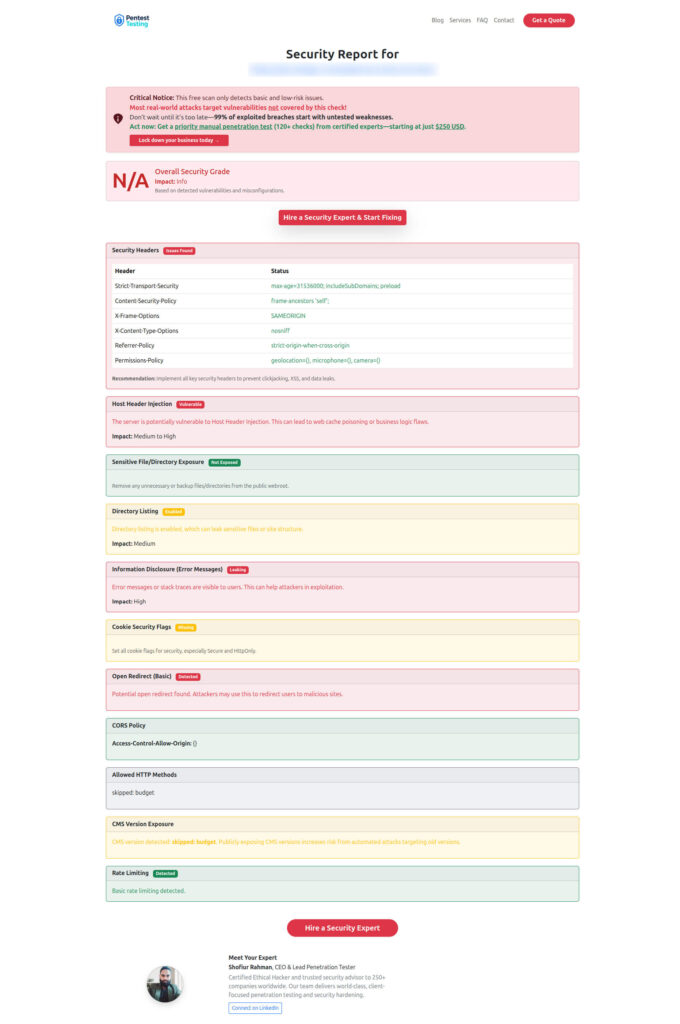
Validate your fixes (use our free scanner)
Example vulnerability report generated by our free tool to check Website Vulnerability
Developer checklists (copy/paste to PR)
Client (React)
- [] No tokens in
localStorage/sessionStorage. - [] Use
credentials: 'include'for cookie-based sessions. - [] Add
X-CSRF-Tokenheader from secure cookie/meta. - [] Never put tokens in URLs or error messages.
- [] Centralize 401 handling and token rotation.
Server (Auth/API)
- [] httpOnly + Secure + SameSite cookies.
- [] Short-lived access tokens; rotate refresh tokens.
- [] Strict CORS, exact origins, no
*with credentials. - [] Verify
aud,iss,exp,iat,nonceas applicable. - [] Rate limit + anomaly detection + session revocation.
Related reading & internal links
- Deep dive on config hardening: Security Misconfiguration in WordPress — relevant for API gateways & reverse proxies too.
🔗 https://www.pentesttesting.com/security-misconfiguration-in-wordpress/ - From our own archive on Cybersrely (great companions to this topic):
- CSP Bypass in React.js → https://www.cybersrely.com/csp-bypass-in-react-js/
- Stop XSSI Attack in React.js → https://www.cybersrely.com/stop-xssi-attack-in-react-js/
- Stop Session Replay Attack in React.js → https://www.cybersrely.com/stop-session-replay-attack-in-react-js/
- Unvalidated Redirects and Forwards in TypeScript → https://www.cybersrely.com/unvalidated-redirects-and-forwards-in-typescript/
These posts complement Weak API Authentication in React.js by covering session abuse, content security pitfalls, and redirect exploitation chains.
Service pages (backlinks & how we can help)
Managed IT Services — Stabilize the foundation
We implement least-privilege, SSO, identity governance, and secure networking that reduce the blast radius of Weak API Authentication in React.js incidents.
🔗 https://www.pentesttesting.com/managed-it-services/
AI Application Cybersecurity — Secure LLM/API integrations
If your React app calls AI backends, we harden auth, key management, and request signing to prevent prompt-proxy abuse and model-gate bypass.
🔗 https://www.pentesttesting.com/ai-application-cybersecurity/
Offer Cybersecurity Service to Your Client — White-label options
Agencies can resell our audits, pentests, and hardening packages (including React/API auth reviews) under your brand.
🔗 https://www.pentesttesting.com/offer-cybersecurity-service-to-your-client/
Contact Us — Fast help from specialists
Need a focused review for Weak API Authentication in React.js in your stack? Reach out and we’ll scope it quickly.
🔗 https://www.cybersrely.com/contact-us/
Bonus: More secure code snippets
Fetch with CSRF + retries
async function safePost(url, data) {
const csrf = document.cookie.match(/(?:^|;\s*)csrf=([^;]+)/)?.[1];
for (let i = 0; i < 2; i++) {
const res = await fetch(url, {
method: 'POST',
credentials: 'include',
headers: { 'Content-Type': 'application/json', 'X-CSRF-Token': csrf || '' },
body: JSON.stringify(data)
});
if (res.status !== 401) return res;
await fetch('/api/auth/refresh', { method: 'POST', credentials: 'include' });
}
throw new Error('Unauthorized');
}Memory-only access token (fallback design)
let accessToken = null; // memory only
export function setAccessToken(t) { accessToken = t; }
export function getAccessToken() { return accessToken; }Audience/issuer checks (server pseudo)
function validateJwtClaims(decoded) {
if (decoded.aud !== 'api.example.com') throw new Error('aud mismatch');
if (decoded.iss !== 'https://idp.example.com') throw new Error('iss mismatch');
if (decoded.exp * 1000 < Date.now()) throw new Error('expired');
}Strict CSP to reduce XSS → token theft risk
<meta http-equiv="Content-Security-Policy"
content="default-src 'self'; script-src 'self'; connect-src 'self' https://api.example.com; object-src 'none'; base-uri 'none'; frame-ancestors 'none'; upgrade-insecure-requests">Pro tip: Bookmark this page and the checklists. Weak API Authentication in React.js is preventable when you apply these 10 best fixes consistently across your stack.
🔐 Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Find answers to commonly asked questions about Weak API Authentication in React.js.
Pingback: Best 7 Ways to Stop XSSI Attack in React.js