Best 5 Ways for CSRF Prevention in React.js [With Examples]
In today’s web landscape, security vulnerabilities are everywhere. One major yet often overlooked threat is Cross-Site Request Forgery (CSRF), especially in modern frontend frameworks like React.js. In this blog post, we’ll cover everything you need to know about CSRF prevention in React.js, along with multiple coding examples to make your app more secure and resilient.
![Best 5 Ways for CSRF Prevention in React.js [With Examples] Best 5 Ways for CSRF Prevention in React.js [With Examples]](https://www.cybersrely.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/04/Best-5-Ways-for-CSRF-Prevention-in-React.js-With-Examples-1024x683.webp)
If you’re serious about building secure web applications, mastering CSRF prevention is a must.
What is CSRF?
Cross-Site Request Forgery (CSRF) is a type of attack where a malicious website tricks a user’s browser into performing an unwanted action on a trusted site where the user is authenticated. This could mean transferring money, changing an email address, or worse.
In React.js applications, CSRF attacks can be especially dangerous if not properly mitigated because React usually handles the frontend while backend APIs are exposed for interaction.
Why CSRF Prevention in React.js Matters
React is a frontend library, but any frontend can be an easy target for attackers if it’s not integrated correctly with secure API calls. That’s why applying CSRF prevention in React.js is not just best practice—it’s necessary for safe app development.
How to Implement CSRF Prevention in React.js
Let’s dive into the 5 best methods for CSRF prevention in React.js, complete with coding examples.
1. Use SameSite Cookie Attribute
The SameSite attribute tells the browser to restrict cookies to first-party contexts only, making it much harder for attackers to exploit authentication cookies.
Example: Setting SameSite Cookies
On the server side (Node.js/Express example):
app.use(session({
secret: 'your_secret_key',
resave: false,
saveUninitialized: true,
cookie: {
sameSite: 'strict', // 'lax' or 'strict' recommended
secure: true
}
}));This way, cookies won’t be sent for cross-origin requests, massively lowering CSRF risks.
React Tip: Always ensure API calls are made with credentials: 'include' if you’re relying on cookies.
fetch('https://your-api.com/data', {
method: 'GET',
credentials: 'include'
})
.then(response => response.json())
.then(data => console.log(data))
.catch(error => console.error(error));2. Anti-CSRF Tokens
The most traditional and strongest defense is generating a CSRF token and validating it on every state-changing request (like POST, PUT, DELETE).
Example: Using CSRF Token in React.js
In your React component:
const csrfToken = document.querySelector('meta[name="csrf-token"]').getAttribute('content');
fetch('/api/secure-action', {
method: 'POST',
headers: {
'Content-Type': 'application/json',
'CSRF-Token': csrfToken
},
body: JSON.stringify({ key: 'value' })
})
.then(response => response.json())
.then(data => console.log(data));And in your backend (Express example):
const csrf = require('csurf');
app.use(csrf());
app.post('/api/secure-action', (req, res) => {
res.json({ message: 'Action completed securely' });
});Best Practice: Refresh the CSRF token periodically to keep the security even tighter.
3. Implement Double Submit Cookies
Instead of only sending a CSRF token in the body, you can also store it in a cookie, and send it manually with every request.
Example: Double Submit Cookie Pattern
React code:
const csrfToken = Cookies.get('csrfToken');
fetch('/api/update-profile', {
method: 'POST',
headers: {
'X-CSRF-Token': csrfToken,
'Content-Type': 'application/json'
},
body: JSON.stringify({ username: 'newUsername' }),
credentials: 'include'
});The backend must validate that both the token in the header and the cookie match.
HomePage Screenshot of our Website Vulnerability Scanner:
4. Protect All State-Changing HTTP Methods
Only allowing GET requests without CSRF protection can save you from tons of vulnerabilities. Protect POST, PUT, PATCH, and DELETE methods strictly.
Example: Axios Interceptors for Security Headers
Set up an interceptor in Axios:
import axios from 'axios';
axios.interceptors.request.use(config => {
config.headers['X-Requested-With'] = 'XMLHttpRequest';
return config;
});Adding X-Requested-With header helps the server distinguish legitimate AJAX requests from forged ones.
5. Content Security Policy (CSP) and CORS Headers
Setting strict CSP and CORS headers helps prevent data leaks and cross-origin attacks.
Example CSP header in Node.js:
app.use((req, res, next) => {
res.setHeader("Content-Security-Policy", "default-src 'self'");
next();
});Proper CORS configuration:
app.use(cors({
origin: 'https://your-react-frontend.com',
credentials: true
}));Best Practices Summary for CSRF Prevention in React.js
- Enable SameSite on cookies.
- Always use CSRF tokens.
- Consider double-submit cookies for extra security.
- Restrict state-changing methods and validate requests.
- Set CSP and CORS headers properly.
By applying these techniques, you can dramatically increase the security of your React.js applications.
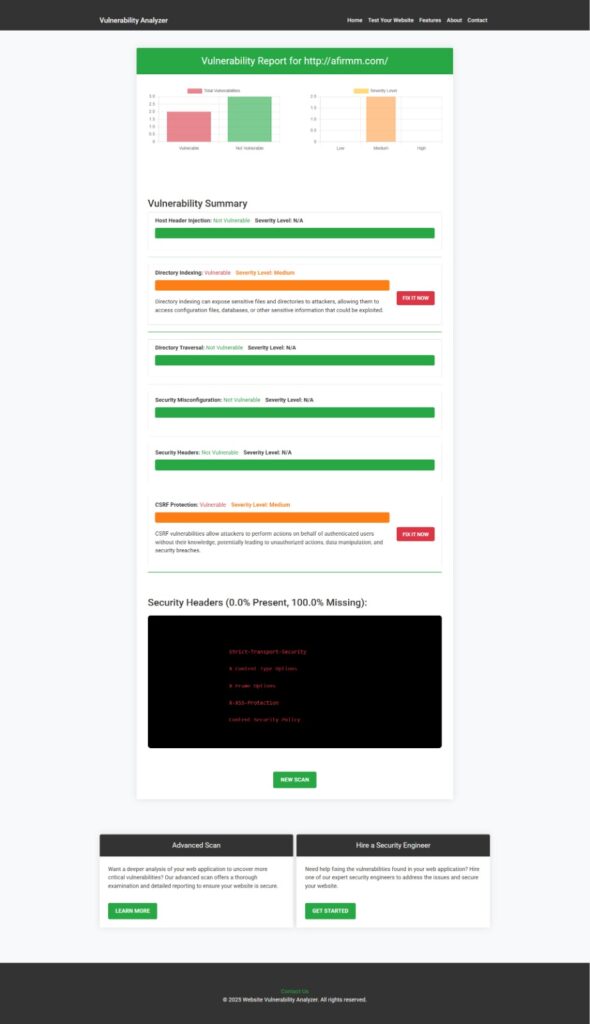
Sample Vulnerability Assesment Report generated by our tool to check Website Vulnerability:
Explore More Security Insights
If you found this guide helpful, check out some of our other detailed posts:
- Prevent Cross-Site Scripting in React.js
- Prevent XML Injection in TypeScript
- Prevent IDOR Vulnerability in React.js
- Fix Broken Authentication in RESTful APIs
- Contact Us for Penetration Testing Services
Additionally, for deeper insights into securing your Laravel apps, read our specialized guide:
👉 File Inclusion Vulnerability in Laravel
Conclusion
CSRF prevention in React.js is crucial for building secure applications. Developers must not rely solely on React’s capabilities but must integrate backend security practices properly. By applying the best 5 methods shared here, you ensure your users’ data and sessions are safe.
Remember: Security is not a one-time action—it’s an ongoing effort. Stay updated, test your apps regularly, and never compromise when it comes to protecting user trust.
✅ Try our free tool for Website Security check today and detect vulnerabilities before attackers do!
Pingback: Prevent IDOR Vulnerability in React.js with Best 7 Tips