Web Cache Deception Attack in React.js — A Deep-Dive with Code (and Practical Fixes)
If your React app uses CDNs, proxies, or aggressive browser caching, you might be one misconfiguration away from a Web Cache Deception Attack in React.js. In this guide, we’ll break down how the attack works in modern React stacks (CSR, SSR/SSG, edge), then implement 10 Best fixes with concrete code you can paste into production. We’ll also show you how to validate your defenses using a free scanner.

What is a Web Cache Deception (WCD) attack?
A Web Cache Deception Attack exploits a mismatch between how your app interprets URLs and how your caching layer (browser, CDN, reverse proxy) stores responses. An attacker appends a fake static extension (e.g., /account/overview**.css**) to a sensitive route. Your app still returns personalized HTML (because routing ignores the fake extension), but the cache may treat it like a static asset and store it publicly. The next visitor who requests that deceptive URL can receive someone else’s private content from the cache.
Why React apps are exposed:
- Single-page apps often rely on wildcard routing;
/anythingcan resolve to the same index file. - CDNs frequently apply permissive caching rules for files ending in
.css,.js,.jpg, etc. - Authentication state may be tied to cookies/headers the cache doesn’t vary on.
Bottom line: In a Web Cache Deception Attack, the attacker tricks your cache into treating private pages as public assets.
Quick demo: how it could happen
- User is signed in at
/account/overview. - Attacker lures them to click
/account/overview.css(or/account/overview;style=css). - Your React app (or Next.js app) still returns the HTML dashboard.
- Misconfigured cache stores it publicly (because “looks like CSS”).
- Anyone who fetches that URL later may see cached private HTML.
Fix #1: Deny deceptive “static-looking” URLs on sensitive routes
At the edge (CDN, load balancer, proxy) deny or bypass cache for sensitive paths if the URL ends with a static extension.
NGINX example
# Block static-like suffixes on sensitive paths (prevents WCD)
location ~* ^/(account|settings|user|orders)/.*\.(?:css|js|png|jpg|jpeg|gif|svg|ico|map)$ {
return 404;
}
# Default: don't cache authenticated pages
set $no_cache 0;
if ($http_cookie ~* "session=|auth=|jwt=") { set $no_cache 1; }
location / {
proxy_pass http://app_upstream;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for;
proxy_set_header Host $host;
# For authenticated traffic, disable cache and vary by cookies
proxy_no_cache $no_cache;
proxy_cache_bypass $no_cache;
add_header Cache-Control "no-store, private" always;
add_header Vary "Cookie, Authorization" always;
}This eliminates the easiest Web Cache Deception Attack in React.js variant by refusing suspicious extensions on sensitive routes.
Fix #2: React Router guard + server deny-list
In CSR-only deployments, React Router must not be your only line of defense. Add a deny-list check server-side.
React Router snippet (defense-in-depth)
// AppRoutes.tsx
import { Navigate, useLocation } from "react-router-dom";
import { useAuth } from "./auth";
const SENSITIVE_SEGMENTS = [/^\/account/, /^\/settings/, /^\/user/];
function isDeceptivePath(pathname: string) {
const looksStatic = /\.(css|js|png|jpg|jpeg|gif|svg|ico|map)$/i.test(pathname);
const hitsSensitive = SENSITIVE_SEGMENTS.some(rx => rx.test(pathname));
return looksStatic && hitsSensitive;
}
export function ProtectedRoute({ children }: { children: JSX.Element }) {
const { user } = useAuth();
const { pathname } = useLocation();
if (isDeceptivePath(pathname)) {
return <Navigate to="/404" replace />;
}
if (!user) return <Navigate to="/login" replace />;
return children;
}Note: Client-side checks are bypassable; keep the server/edge rules as the source of truth.
📸 Screenshot of our Free Website Vulnerability Scanner :
Fix #3: Express/Node server headers for private content
Make sensitive endpoints uncacheable and vary on auth.
// server.ts
import express from "express";
import helmet from "helmet";
const app = express();
app.use(helmet());
function noStorePrivate(req, res, next) {
res.set("Cache-Control", "no-store, private");
res.set("Pragma", "no-cache");
res.set("Vary", "Cookie, Authorization");
next();
}
app.use("/account", noStorePrivate);
app.use("/settings", noStorePrivate);
app.use("/api", noStorePrivate);
// Static assets: long-lived public cache (safe)
app.use("/assets", express.static("dist/assets", {
setHeaders(res) {
res.setHeader("Cache-Control", "public, max-age=31536000, immutable");
}
}));
app.get("*", (req, res) => {
// render your React app shell
res.sendFile("dist/index.html", { root: __dirname });
});
app.listen(3000);These headers dramatically reduce the chance of a Web Cache Deception Attack in React.js.
Fix #4: Next.js headers & middleware (SSR/SSG)
If you’re on Next.js, treat sensitive pages differently.
next.config.mjs
export default {
async headers() {
return [
{
source: "/(account|settings|user)/(.*)",
headers: [
{ key: "Cache-Control", value: "no-store, private" },
{ key: "Pragma", value: "no-cache" },
{ key: "Vary", value: "Cookie, Authorization" },
],
},
{
source: "/_next/static/(.*)",
headers: [
{ key: "Cache-Control", value: "public, max-age=31536000, immutable" },
],
},
];
},
};Edge middleware to reject deceptive suffixes
// middleware.ts
import { NextResponse } from "next/server";
import type { NextRequest } from "next/server";
const STATIC_EXT = /\.(css|js|png|jpg|jpeg|gif|svg|ico|map)$/i;
const SENSITIVE = /^\/(account|settings|user)\//;
export function middleware(req: NextRequest) {
const url = new URL(req.url);
if (SENSITIVE.test(url.pathname) && STATIC_EXT.test(url.pathname)) {
return new NextResponse(null, { status: 404 });
}
return NextResponse.next();
}Fix #5: Service Worker safe caching strategy
Never cache authenticated HTML/API responses.
// service-worker.js
self.addEventListener("fetch", (event) => {
const req = event.request;
const url = new URL(req.url);
const isSensitive = /^\/(account|settings|user|api)\//.test(url.pathname);
const looksStatic = /\.(css|js|png|jpg|jpeg|gif|svg|ico|map)$/i.test(url.pathname);
// Always bypass cache for sensitive content
if (isSensitive) {
event.respondWith(fetch(req, { cache: "no-store", credentials: "include" }));
return;
}
// Cache-only truly static assets
if (looksStatic) {
event.respondWith(
caches.open("static-v1").then(async (cache) => {
const cached = await cache.match(req);
if (cached) return cached;
const resp = await fetch(req);
// Honor response headers before caching
if (/max-age=\d+|immutable/.test(resp.headers.get("Cache-Control") || "")) {
cache.put(req, resp.clone());
}
return resp;
})
);
return;
}
// For everything else, network-first without storing
event.respondWith(fetch(req, { cache: "no-store" }));
});This eliminates a large class of Web Cache Deception risks introduced by aggressive offline strategies.
Fix #6: Client fetch options for sensitive calls
Set explicit cache directives client-side (defense-in-depth).
// api.ts
export async function getProfile() {
const res = await fetch("/api/profile", {
method: "GET",
credentials: "include",
cache: "no-store",
headers: {
"Accept": "application/json",
},
});
if (!res.ok) throw new Error("Failed to load profile");
return res.json();
}Fix #7: Normalize URLs (avoid deceptive extensions)
Strip fake static suffixes server-side before routing.
// normalize.ts (Express middleware)
const STATIC_EXT = /\.(css|js|png|jpg|jpeg|gif|svg|ico|map)$/i;
const SENSITIVE = /^\/(account|settings|user|orders)\//;
export function normalizeUrls(req, _res, next) {
if (SENSITIVE.test(req.path) && STATIC_EXT.test(req.path)) {
// Explicitly block
const err = new Error("Not found");
// @ts-ignore
err.status = 404;
return next(err);
}
return next();
}Fix #8: Vary correctly and mark privacy
Always vary on cookies and auth, and set private vs public correctly.
Cache-Control: no-store, private
Pragma: no-cache
Vary: Cookie, Authorization, Accept-EncodingDo this on every sensitive response. This is core to stopping a Web Cache Deception.
Fix #9: CDN rules (example patterns)
At your CDN (e.g., Cloudflare/Fastly/Akamai):
- Bypass cache when:
- Path matches
/account/*,/settings/*,/api/*,/user/* - Request has cookie
session=*or headerAuthorization=*
- Path matches
- Never cache responses with:
Cache-Control: no-store,private, orSet-Cookie
- Block URLs under sensitive paths that end with static file extensions.
These rules shut down cache poisoning and reduce Web Cache Deception Attack in React.js opportunities.
Fix #10: Test the hard way (curl + your scanner)
Try to pull sensitive pages using deceptive URLs, then verify they weren’t cached:
# First hit (should not be cached)
curl -I -H "Cookie: session=abc" https://yourapp.com/account/overview.css
# Second hit (no cookie, should NOT return the first user's HTML)
curl -I https://yourapp.com/account/overview.css📸 Sample assessment report generated by our free tool to check Website Vulnerability:
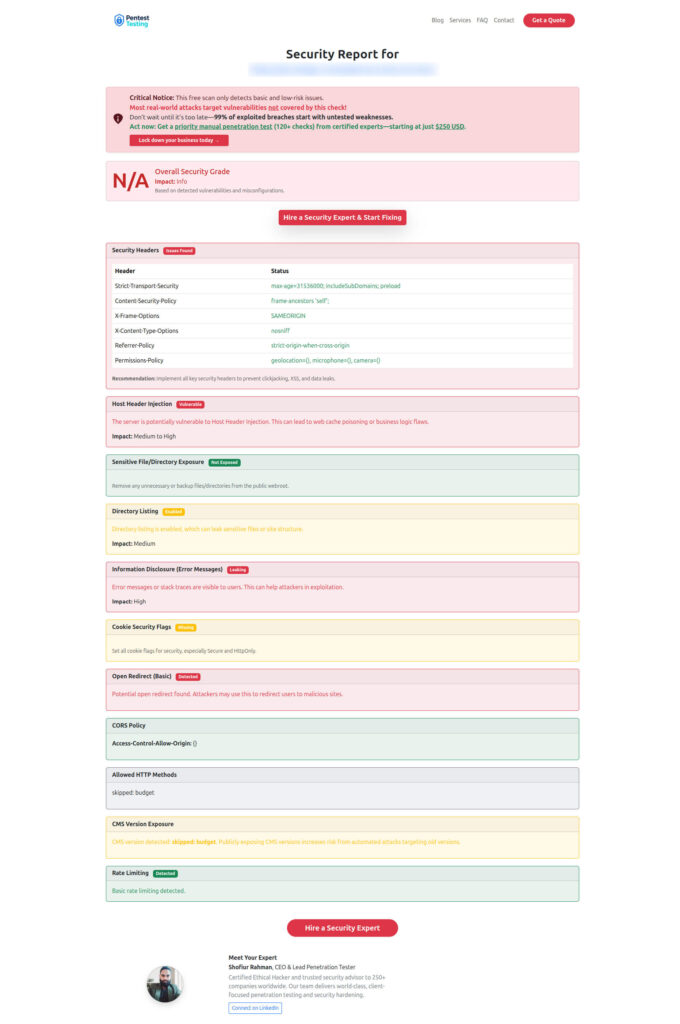
Run a full scan with our free tool to catch weak caching headers or exposed endpoints early.
Real-world React patterns that invite WCD
- SPA fallback everywhere (all paths return
index.html), but CDN treats*.cssas public & cacheable. - SSR/SSG static export where sensitive sections aren’t properly excluded.
- Service Worker caching HTML/API without respect to auth state.
- Mixed caching: reverse proxy caches HTML when it sees
.jsin the path (path-based heuristics). - Lack of
Vary: different users’ responses look identical to the cache.
Keep these in mind whenever you see the phrase Web Cache Deception Attack in React.js in audits and pentest reports.
Related learning (from our blogs)
- JWT Attacks in React.js — deep dive into token misuse and mitigations:
https://www.cybersrely.com/jwt-attacks-in-react-js/ - Prevent NoSQL Injection in React.js — input validation and API-layer hardening:
https://www.cybersrely.com/prevent-nosql-injection-in-react-js/ - Prevent Cache Poisoning in TypeScript — header strategies & edge rules:
https://www.cybersrely.com/prevent-cache-poisoning-in-typescript/ - Learn 10 Best Ways to Prevent XML Injection in React.js—safe parsing, validation, and copy-paste code to harden your app:
https://www.cybersrely.com/prevent-xml-injection-in-react-js/
Also see our practical guide on related auth exposure vectors:
Fix IDOR Vulnerability in WordPress — https://www.pentesttesting.com/fix-idor-vulnerability-in-wordpress/
These tie in naturally with preventing a Web Cache Deception Attack in React.js by ensuring sensitive content exposure is minimized across layers.
Services you can leverage (add backlinks)
Managed IT Services (Operations hardening)
Harden infrastructure, standardize headers, and audit proxies/CDNs continuously.
https://www.pentesttesting.com/managed-it-services/
AI Application Cybersecurity (LLM & AI app risks)
Secure AI-driven features, classify content sensitivity, and enforce cache policies dynamically.
https://www.pentesttesting.com/ai-application-cybersecurity/
Offer Cybersecurity Service to Your Client (Agency Partnership)
White-label testing & dev-sec enablement.
https://www.pentesttesting.com/offer-cybersecurity-service-to-your-client/
Talk to Us
Need a targeted review to ensure you’re safe from a Web Cache Deception Attack in React.js?
https://www.cybersrely.com/contact-us/
Extra code: defense-in-depth checks
Deny deceptive URLs at the router middleware (Express)
// deceptive-guard.ts
import type { Request, Response, NextFunction } from "express";
const SENSITIVE_PATHS = /^(\/(account|settings|user|orders))/i;
const STATIC_EXTS = /\.(css|js|png|jpg|jpeg|gif|svg|ico|map)$/i;
export function deceptiveGuard(req: Request, res: Response, next: NextFunction) {
if (SENSITIVE_PATHS.test(req.path) && STATIC_EXTS.test(req.path)) {
return res.status(404).send("Not found");
}
next();
}Helmet & strict transport
import helmet from "helmet";
app.use(helmet({
contentSecurityPolicy: false, // customize as needed
hsts: { maxAge: 31536000, includeSubDomains: true, preload: true },
}));Strict separation of static vs dynamic
// Static (public, long cache)
app.use("/static", express.static("build/static", {
immutable: true,
maxAge: "365d",
}));
// Dynamic shell (private)
app.get(["/account/*", "/settings/*", "/user/*"], (req, res) => {
res.set({
"Cache-Control": "no-store, private",
"Vary": "Cookie, Authorization",
});
// render SSR or serve index.html with user boot data server-side
res.send(renderHtmlForUser(req.user));
});Unit test for headers (Jest)
test("account pages are never cacheable", async () => {
const res = await request(app).get("/account/overview.css").set("Cookie", "session=abc");
expect(res.status).toBe(404); // blocked deceptive suffix
});
test("api responses are private", async () => {
const res = await request(app).get("/api/profile").set("Cookie", "session=abc");
expect(res.headers["cache-control"]).toMatch(/no-store/);
expect(res.headers["vary"]).toMatch(/cookie/i);
});These tests help ensure no regressions reintroduce a Web Cache Deception Attack in React.js.
Final checklist (paste into your issue tracker)
- Block static-like suffixes under sensitive routes at CDN/proxy.
- Mark dynamic/auth responses
no-store, privateandVary: Cookie, Authorization. - Separate static vs dynamic routes; immutable caching only for assets.
- Service worker never caches auth content.
- Add unit tests for headers and deceptive paths.
- Validate with curl and the free scanner.
This complete guide and code pack should help you spot and fix a Web Cache Deception Attack in React.js before it becomes a breach. If you’d like a quick review of your headers, CDN config, or service worker strategy, reach out via https://www.cybersrely.com/contact-us/ — we’re happy to help.
🔐 Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Find answers to commonly asked questions about Web Cache Deception Attack in React.js.
Pingback: Prevent XML Injection in React.js: 10 Proven Ways