7 Best Ways to Stop Session Replay Attack in React.js
What is a “Session Replay Attack in React.js”?
A Session Replay Attack in React.js happens when code (often a third-party “session recording” script) captures the DOM, clicks, mouse moves, keystrokes, and network events from your React SPA—sometimes including sensitive fields. If such a script is over-permissive, injected via a compromised dependency/CDN, misconfigured, or loaded without consent, it can leak PII and security tokens to external servers. Academic and industry reporting shows that poorly configured replay scripts have captured passwords, credit-card digits, and health data in the wild.

React by itself doesn’t prevent this because browsers execute any allowed script. The defense is defense-in-depth: CSP, integrity checks, consent-gated loading, cookie hardening, and field-level redaction in components. MDN/OWASP guidance reinforces these practices as modern web security baselines.
TL;DR for busy teams
- Treat Session Replay Attack in React.js as a data-exfil risk, not just analytics.
- Allowlist scripts via CSP, pin third-party assets with SRI, and load replay SDKs only after consent.
- Redact sensitive inputs at the component level, and scrub payloads.
- Harden cookies (HttpOnly, Secure, SameSite) and avoid exposing tokens to JS.
Threat model: how React apps get exposed
- Direct embed of a session replay SDK with broad capture defaults.
- Supply-chain injection via a dependency/CDN that adds beaconing code.
- Stored/Reflected XSS that drops “replay” code on your SPA route. CSP reduces blast radius.
- Leaky state (tokens in
localStorageor accessible cookies) that a script can read. - Non-consented loading (privacy/regulatory risk + trust erosion).
Quick look at our free Website Vulnerability Scanner tool page
The 7 Best Ways to Stop Session Replay Attack in React.js
1) Load replay scripts only after consent
Gate any session recording behind explicit user consent and a feature flag.
// src/consent/ConsentGate.tsx
import { useEffect } from "react";
type Props = { consentGiven: boolean };
export default function ConsentGate({ consentGiven }: Props) {
useEffect(() => {
if (!consentGiven) return;
// Dynamically load the replay SDK only after consent
const s = document.createElement("script");
s.src = "https://example-cdn.com/replay-sdk.min.js";
s.async = true;
s.crossOrigin = "anonymous";
s.integrity = "sha384-<SRI-HASH>"; // Pin with SRI
document.head.appendChild(s);
return () => { document.head.removeChild(s); };
}, [consentGiven]);
return null;
}Why this helps: the script is not even present in the page until the user opts in. Pair with SRI to prevent tampered assets.
2) Enforce a strong CSP (with nonces) and an allowlist
Use server-set Content-Security-Policy. Disallow unsafe-inline and * wildcards; allowlist only what you truly need.
// server/securityHeaders.ts (Node/Express)
import { randomBytes } from "crypto";
import type { Request, Response, NextFunction } from "express";
export function cspWithNonce(req: Request, res: Response, next: NextFunction) {
const nonce = randomBytes(16).toString("base64");
res.locals.nonce = nonce;
const csp = [
"default-src 'self'",
`script-src 'self' 'nonce-${nonce}' https://example-cdn.com`, // allowlisted CDN
"style-src 'self' 'unsafe-inline'", // if you must, or use nonces for styles too
"img-src 'self' data:",
"connect-src 'self' https://api.myapp.com", // limit beacons
"frame-ancestors 'none'",
"base-uri 'self'",
"object-src 'none'",
"upgrade-insecure-requests"
].join("; ");
res.setHeader("Content-Security-Policy", csp);
next();
}Render the nonce in your HTML template:
// server/template.ts
export const html = (nonce: string, reactHtml: string) => `
<!doctype html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8" />
<script nonce="${nonce}">window.__NONCE__='${nonce}'</script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="root">${reactHtml}</div>
<script nonce="${nonce}" src="/static/main.js"></script>
</body>
</html>`;CSP is your second line of defense that limits what any injected or third-party script can do. Configure it server-side (HTTP header) for reliability.
3) Redact and mask sensitive inputs at the component level
Prevent accidental capture of PII by never rendering raw secrets.
// src/components/RedactedInput.tsx
import { useState } from "react";
type Props = {
label: string;
name: string;
type?: "text" | "password" | "tel" | "email";
redact?: boolean; // when true, mask UI and strip value from analytics/hooks
};
export default function RedactedInput({ label, name, type="text", redact=false }: Props) {
const [value, setValue] = useState("");
function onChange(e: React.ChangeEvent<HTMLInputElement>) {
const v = e.target.value;
setValue(v);
if (!redact) {
window.dispatchEvent(new CustomEvent("safe-input-change", { detail: { name, value: v } }));
}
}
return (
<label className="block">
<span className="text-sm">{label}</span>
<input
name={name}
type={type}
value={redact ? value.replace(/./g, "•") : value}
onChange={onChange}
autoComplete="off"
data-redact={redact} // signal to any SDK to skip this field
className="border rounded p-2 w-full"
/>
</label>
);
}Use redact for fields like card numbers, SSNs, recovery codes, and health notes.
4) Harden cookies: HttpOnly + Secure + SameSite
Never expose session tokens to JavaScript; get them out of localStorage.
// server/cookies.ts (Node/Express)
import type { Response } from "express";
export function setSessionCookie(res: Response, token: string) {
res.setHeader("Set-Cookie", [
`session=${token}`,
"Path=/",
"HttpOnly", // JS cannot read
"Secure", // HTTPS only
"SameSite=Strict" // reduces CSRF and cross-site sending
].join("; "));
}MDN:
HttpOnlyprevents JS access;SameSitereduces cross-site leakage. This directly reduces the blast radius of any rogue script attempting to read tokens.
5) Scrub outbound payloads (defense against oversharing)
// src/utils/safeFetch.ts
const PII_KEYS = ["password", "card", "cvv", "ssn", "secret", "token"];
function scrub(obj: any): any {
if (obj == null || typeof obj !== "object") return obj;
if (Array.isArray(obj)) return obj.map(scrub);
return Object.fromEntries(
Object.entries(obj).map(([k, v]) => [
k,
PII_KEYS.some(key => k.toLowerCase().includes(key)) ? "[REDACTED]" : scrub(v)
])
);
}
export async function safeFetch(input: RequestInfo, init: RequestInit & { bodyJson?: any } = {}) {
const { bodyJson, ...rest } = init;
const body = bodyJson ? JSON.stringify(scrub(bodyJson)) : init.body;
return fetch(input, { ...rest, body, headers: { "Content-Type": "application/json", ...(rest.headers||{}) } });
}Use safeFetch for analytics/hooks to ensure sensitive keys aren’t sent.
6) Pin third-party assets with Subresource Integrity (SRI)
If you must pull from a CDN, pin the hash.
<!-- index.html -->
<script
src="https://cdn.example.com/replay-sdk.min.js"
integrity="sha384-<BASE64-HASH>"
crossorigin="anonymous"
defer></script>If the asset changes unexpectedly, the browser drops it. That blocks many injection paths.
7) Block suspicious beaconing via a Service Worker (bonus containment)
You can neuter runaway beacon endpoints even if a script slips through.
// public/sw.js
self.addEventListener("fetch", (event) => {
const url = new URL(event.request.url);
const blockedHosts = ["beacon.example-analytics.com", "collector.example-replay.com"];
if (blockedHosts.includes(url.hostname)) {
event.respondWith(new Response("", { status: 204 })); // swallow the beacon
}
});Register once in your app:
// src/swRegister.ts
export function registerSW() {
if ("serviceWorker" in navigator) {
navigator.serviceWorker.register("/sw.js");
}
}Example report from our free scanner to check Website Vulnerability
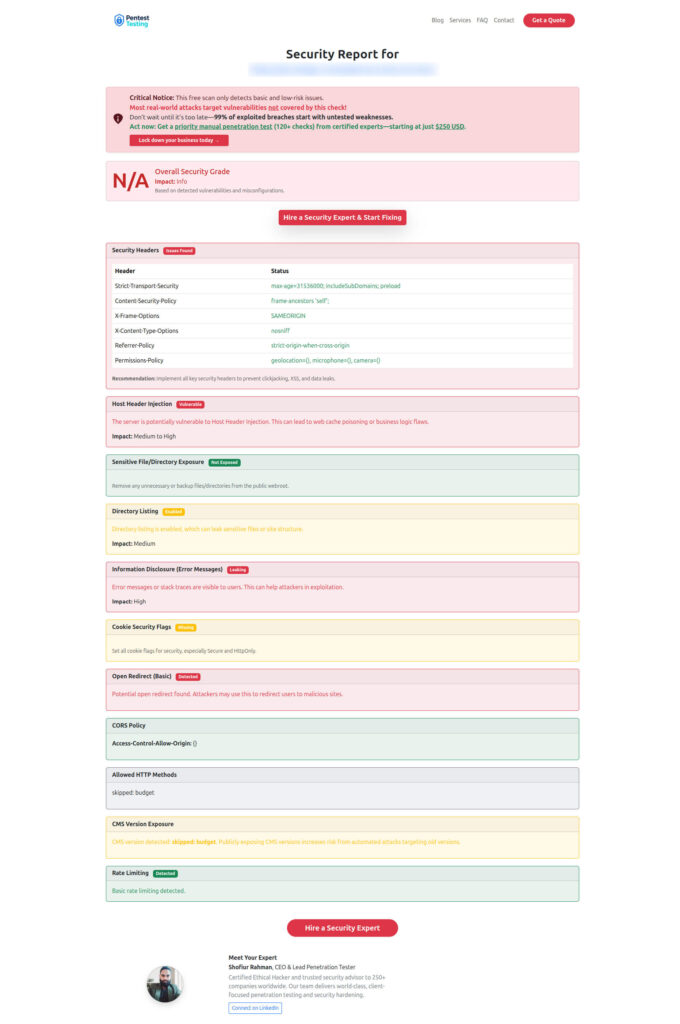
Full React + Express demo: consent-gated replay + CSP + cookie hardening
// server/index.ts
import express from "express";
import path from "path";
import { cspWithNonce } from "./securityHeaders";
import { setSessionCookie } from "./cookies";
const app = express();
app.use(cspWithNonce);
app.use("/static", express.static(path.join(__dirname, "static")));
app.get("/login", (_, res) => {
// Pretend we created a session token server-side:
setSessionCookie(res, "opaque-session-id"); // HttpOnly, Secure, SameSite=Strict
res.redirect("/");
});
app.get("/", (_, res) => {
res.sendFile(path.join(__dirname, "index.html"));
});
app.listen(3000, () => console.log("Server on http://localhost:3000"));// src/App.tsx
import { useState } from "react";
import ConsentGate from "./consent/ConsentGate";
import RedactedInput from "./components/RedactedInput";
import { safeFetch } from "./utils/safeFetch";
export default function App() {
const [consent, setConsent] = useState(false);
return (
<main className="p-6">
<h1 className="text-2xl font-bold">Session Replay Attack in React.js: Live Demo</h1>
<div className="my-4">
<label className="mr-2">Allow session recording?</label>
<input type="checkbox" checked={consent} onChange={e => setConsent(e.target.checked)} />
</div>
<ConsentGate consentGiven={consent} />
<form
onSubmit={async (e) => {
e.preventDefault();
await safeFetch("/api/checkout", { method: "POST", bodyJson: { card: "4111111111111111", name: "Ada" }});
alert("Submitted (card redacted before sending)");
}}
className="space-y-3 max-w-md"
>
<RedactedInput label="Card number" name="card" redact />
<RedactedInput label="Name on card" name="name" />
<button className="px-4 py-2 rounded bg-black text-white">Pay</button>
</form>
</main>
);
}Why this matters (research & guidance)
Independent research documented how session replay scripts captured highly sensitive data on real sites when masking failed or was misconfigured. Solid CSP and SRI, plus strict cookie practices, mitigate many attack paths and leaks.
Related reading and internal resources
- Fix sensitive data exposure in WordPress (good primer on data-exfil risks).
- Previous posts you’ll find useful for React hardening:
Services & backlinks (recommended next steps)
Managed IT Services (Pentest Testing Corp)
Stronger baselines, patch cadence, and endpoint controls reduce the odds of a Session Replay Attack in React.js being introduced in the first place.
AI Application Cybersecurity (Pentest Testing Corp)
Threat-model your LLM/AI features and third-party SDKs; verify no replay or analytics library can siphon prompts or outputs.
White-Label Cybersecurity for Agencies (Pentest Testing Corp)
Offer clients secure SPA builds with CSP, SRI, and cookie hardening baked in.
Partner with us>>
Need help now?
Get a tailored review of your React routes, headers, and 3rd-party scripts, plus a remediation plan to eliminate Session Replay Attack in React.js vectors. Contact us>>
Developer checklist (copy/paste into your issue tracker)
- Load any recording SDK only after consent; default off.
- Implement CSP with nonces; allowlist only needed hosts; no
unsafe-eval. - Add SRI to all CDN scripts; verify hashes in CI.
- Make session tokens HttpOnly + Secure + SameSite=Strict.
- Redact inputs and scrub payloads before sending analytics.
- Register a Service Worker to sinkhole unexpected beacon hosts.
- Run our free scanner for Website Security check to validate headers and script hygiene.
Final note
If you implement the seven steps above, you’ll dramatically lower the chances of a Session Replay Attack in React.js and improve your overall security posture—without losing the analytics you actually need.
🔐 Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Find answers to commonly asked questions about Session Replay Attack in React.js.