Best 7 Ways to Prevent DNS Rebinding Attack in React.js 🔐
What Is a DNS Rebinding Attack in React.js?
A DNS Rebinding Attack in React.js is a serious browser-based vulnerability where attackers bypass the same-origin policy by manipulating DNS responses. This allows them to interact with internal services or private networks from a public-facing React app — leading to unauthorized access, data leaks, or even system compromise.

Imagine your React.js application fetching data from api.myapp.com. An attacker registers a domain like attacker.com, manipulates DNS entries, and tricks your browser into treating attacker.com as your internal IP, say 192.168.1.1. Boom — they now access internal interfaces from within your app.
Why DNS Rebinding Is Dangerous for React Developers
React apps often communicate with APIs, load dynamic content, and are deployed behind proxies or cloud firewalls — making them prime targets for DNS rebinding. Attackers exploit:
- Misconfigured CORS headers
- Open internal ports
- Lack of strict origin validation
- Third-party integrations that trust any domain
React developers must understand DNS rebinding in React.js to protect sensitive data and APIs.
How DNS Rebinding Attack Works: Step-by-Step
- Attacker registers a malicious domain (e.g., evilsite.com)
- Hosts a React-based exploit script on the domain
- The DNS server first resolves evilsite.com to the attacker’s server IP
- After initial load, the DNS server updates evilsite.com to resolve to 127.0.0.1 or internal IPs
- Browser thinks it’s the same domain (due to cached origin)
- Now the attacker’s script can make XMLHttpRequests to localhost/internal services
🧪 Code Example: A Malicious React DNS Rebinding Script
// attacker React script
useEffect(() => {
setInterval(() => {
fetch('http://evilsite.com:8080/api/data') // initially
.then(res => res.text())
.then(console.log);
}, 3000); // loop to access internal API after DNS switch
}, []);This script appears harmless but, when rebinding occurs, it silently targets your internal services.
🔐 Best 7 Ways to Prevent DNS Rebinding Attack in React.js
1. Use Hostname Whitelisting on Server Side
// Node.js example with Express
const allowedHosts = ['myapp.com'];
app.use((req, res, next) => {
const host = req.hostname;
if (!allowedHosts.includes(host)) return res.status(403).send('Forbidden');
next();
});DNS rebinding won’t help if your backend rejects unknown hostnames.
2. Block Private IP Access in Browser Using CSP
<meta http-equiv="Content-Security-Policy" content="default-src 'self'; connect-src https://api.myapp.com;">Avoid allowing wildcard connect-src * which DNS rebinding relies on. CSP helps contain what origins your app connects to.
3. Validate CORS Origin Strictly
const allowedOrigins = ['https://myapp.com'];
app.use((req, res, next) => {
const origin = req.get('Origin');
if (!allowedOrigins.includes(origin)) {
return res.status(403).send('Blocked by CORS policy');
}
res.header('Access-Control-Allow-Origin', origin);
next();
});DNS rebinding attempts from evilsite.com will get blocked here.
4. Use Subdomain Isolation
Isolate sensitive content or admin panels on different subdomains and enforce CORS headers on all inter-subdomain communication.
5. Limit DNS TTLs for Public Domains
If you’re serving React apps from CDN or custom domains, configure low TTL values to detect anomalies or flush DNS cache quicker.
6. Inspect Internal Ports
Use scanning tools to check if your React frontend can reach internal IP ranges or ports. You can automate this using our free vulnerability scanner.
📸 Screenshot of your Website Vulnerability Scanner tool:
Try scanning your React app now to reveal hidden DNS rebinding vulnerabilities. This tool reports DNS hijack attempts, header misconfigurations, and access to local ports.
7. Monitor and Log Suspicious DNS Requests
Use DNS logging tools or browser-based telemetry to track abnormal DNS requests from your app.
📸 Screenshot of a sample vulnerability report generated by our tool to check Website Vulnerability:
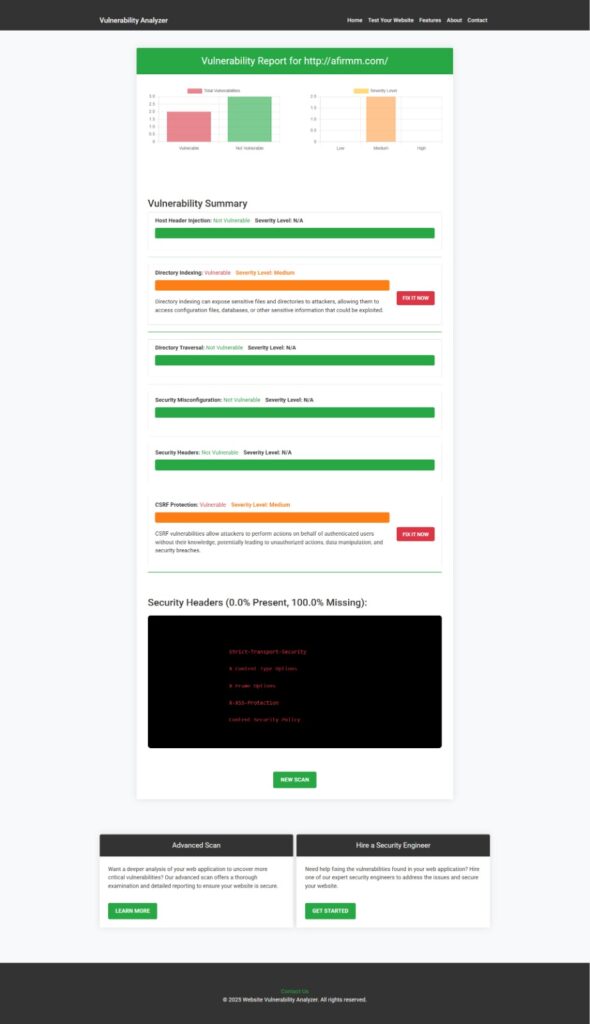
Real-World Case: Exposing IoT Devices with DNS Rebinding
Attackers used DNS rebinding against smart thermostats exposed through React-based dashboards. The attack targeted 127.0.0.1:3000/admin, granting full access to internal APIs. A simple filter on req.hostname could have stopped this!
🧠 Related Blogs on React Security
Looking to improve your React app’s security even more?
- 🔄 Prevent Race Condition in React.js
- 🌐 Prevent Host Header Injection in React.js
- 💡 Prevent Host Header Injection in TypeScript
- 🛡️ Prevent Command Injection Attack in React.js
These articles dive deeper into practical code examples and are must-reads if you’re serious about React security.
🔁 Explore Laravel Redirection Security
Are you working on both Laravel and React?
Check out our blog on Unvalidated Redirects and Forwards in Laravel to secure both ends of your stack.
🚀 Need Expert Help? Try Our Security Services
🔍 Web Application Penetration Testing Services
Our experts identify DNS rebinding issues before attackers do.
🤝 Offer Cybersecurity Services to Your Clients
Expand your agency’s offerings by white-labeling our pentesting solutions.
📨 Contact Us for custom React security audits, penetration tests, and more.
Final Thoughts
DNS Rebinding Attack in React.js is subtle but dangerous — and surprisingly easy to execute without proper defense. By implementing strict CORS policies, whitelisting hosts, setting correct CSP headers, and scanning your app regularly, you protect both users and infrastructure.
Want to test your React app today?
📩 Use our Free Website Security Scanner to scan for DNS rebinding vulnerabilities now.
Pingback: Business Logic Vulnerabilities in Laravel: Best 7 Solutions
Pingback: Prevent Command Injection Attack in React.js: Best 5 Ways