🛡️ Best 7 Ways to Prevent NoSQL Injection in React.js
Introduction to NoSQL Injection in React.js
NoSQL Injection in React.js is a serious security vulnerability that occurs when untrusted user input is passed to NoSQL queries without proper validation or sanitization. Unlike traditional SQL injection, NoSQL injection targets non-relational databases like MongoDB, which are often used in modern JavaScript stacks (e.g., MERN). Because React.js is commonly used on the frontend, poorly handled inputs or insecure API communication can easily lead to injection paths.

What is NoSQL Injection?
NoSQL Injection is an attack where an attacker manipulates a NoSQL query by injecting malicious input. It typically happens when the input sent to a backend API from a React.js front end is used directly in MongoDB or other NoSQL queries.
Here’s a basic example:
// Insecure backend API using Node.js + MongoDB
const user = await db.collection("users").findOne({ username: req.body.username });If this API receives input from a React form without sanitization:
{
"username": { "$ne": null }
}It bypasses authentication and returns the first user found.
Why React.js Apps Are Vulnerable
React.js, being a frontend framework, does not directly interact with databases. However, it’s responsible for collecting user input and passing it to backend APIs. Improper validation on the client side combined with insecure backend practices leads to NoSQL Injection in React.js.
Real-World NoSQL Injection Attack in React.js
1. Insecure React.js Form Submission
// Insecure Login Form
function Login() {
const [username, setUsername] = useState("");
const handleLogin = async () => {
await fetch("/api/login", {
method: "POST",
headers: { "Content-Type": "application/json" },
body: JSON.stringify({ username }),
});
};
return (
<input
type="text"
onChange={(e) => setUsername(e.target.value)}
/>
);
}This input is sent to an insecure Node.js API and used directly in a query:
db.users.findOne({ username: req.body.username });Attack Payload:
{
"username": { "$ne": "" }
}Result: Auth bypass for any user!
🔍 How to Detect NoSQL Injection in React.js Apps
You can detect NoSQL injection vulnerabilities using automated tools like:
✅ Free Website Vulnerability Scanner
Use this scanner to check if your application is vulnerable to NoSQL Injection in React.js and other critical issues.
🔐 Best Practices to Prevent NoSQL Injection in React.js
1. Sanitize Inputs Before Sending to API
Use libraries like validator.js or DOMPurify:
import validator from "validator";
if (validator.isAlphanumeric(username)) {
// safe to send
}2. Use Parameterized Queries on Backend
Example in Node.js:
const sanitizedInput = String(req.body.username);
db.collection("users").findOne({ username: sanitizedInput });3. Validate All Input Types
Avoid implicit casting in MongoDB by explicitly checking types:
if (typeof req.body.username !== "string") {
return res.status(400).send("Invalid input");
}4. Whitelist Allowed Parameters
Only allow specific keys in request bodies:
const allowed = ['username', 'password'];
const isValid = Object.keys(req.body).every(key => allowed.includes(key));5. Disable MongoDB Operators in Queries
Avoid accepting raw JSON directly:
const input = JSON.parse(req.body.username);
if (Object.keys(input).some(k => k.startsWith('$'))) {
throw new Error("Injection attempt");
}6. Use Web Application Firewalls (WAF)
WAFs like Cloudflare or AWS WAF help block malicious NoSQL queries before they reach your backend.
7. Regular Penetration Testing
Ensure periodic pentests are conducted using tools like:
📄 Sample Vulnerability Report
Once scanned, you can generate a detailed report to check Website Vulnerability:
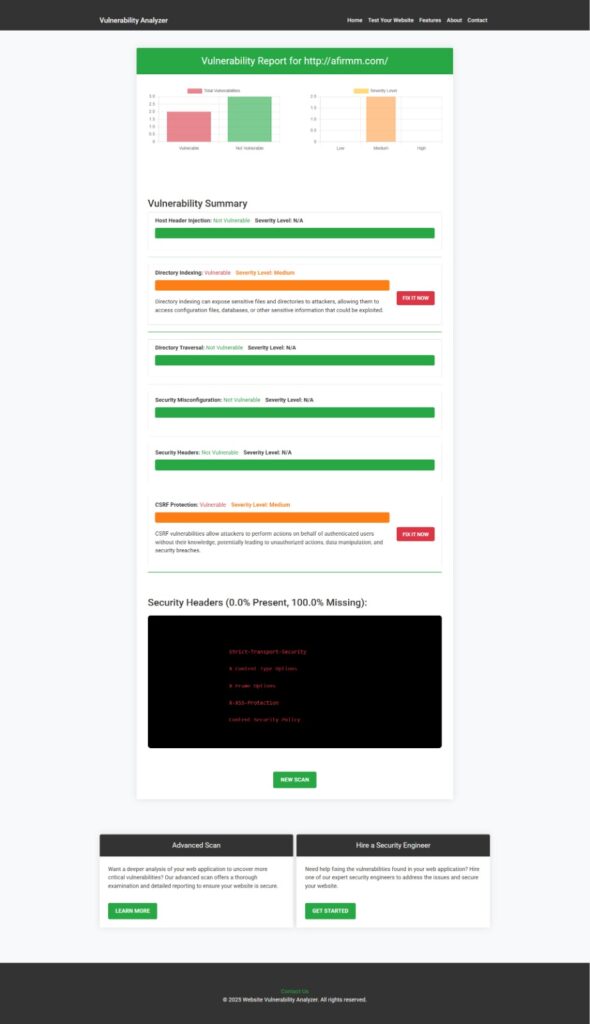
The report includes endpoints tested, parameter injection attempts, and the risk level—helping you take actionable steps.
🔁 Related Blogs You Might Find Useful
- ✅ Insufficient Logging and Monitoring in React.js
- ✅ Prevent Cache Poisoning in React.js
- ✅ Prevent Race Condition in TypeScript
- ✅ Stop Session Replay Attack in Laravel
- ✅ Check for Subdomain Takeover in React.js
🔗 Need Advanced Security for AI-Integrated Apps?
If you’re building AI-powered apps, check our new page on AI Application Cybersecurity:
👉 https://www.pentesttesting.com/ai-application-cybersecurity/
Protect machine learning models, APIs, and data pipelines from logic flaws and injection vectors.
🧩 Partner with Us — Offer Security to Your Clients
Are you a web agency, IT provider, or consultant?
Partner with us to offer full-scale vulnerability assessments to your clients.
📌 https://www.pentesttesting.com/offer-cybersecurity-service-to-your-client/
📬 Get Help or Talk to Our Experts
Facing a potential NoSQL Injection in React.js or other frontend threats? We’re here to help.
📞 Reach out at: https://www.cybersrely.com/contact-us/
Final Thoughts
NoSQL Injection in React.js is often overlooked but highly dangerous. Modern applications using MongoDB, Firebase, or CouchDB are prime targets if inputs are not sanitized properly. Whether you’re working on a side project or managing enterprise applications, it’s crucial to implement the above protections.
By combining client-side validation in React.js and backend hardening, you can stay a step ahead of attackers.
Want a free scan?
Try our free scanner today at https://free.pentesttesting.com/
Or DM us for a consultation. Stay safe!
Pingback: Prevent Cache Poisoning in React.js: 7 Proven Techniques